How Do Doctors Diagnose Gynecomastia in Riyadh?
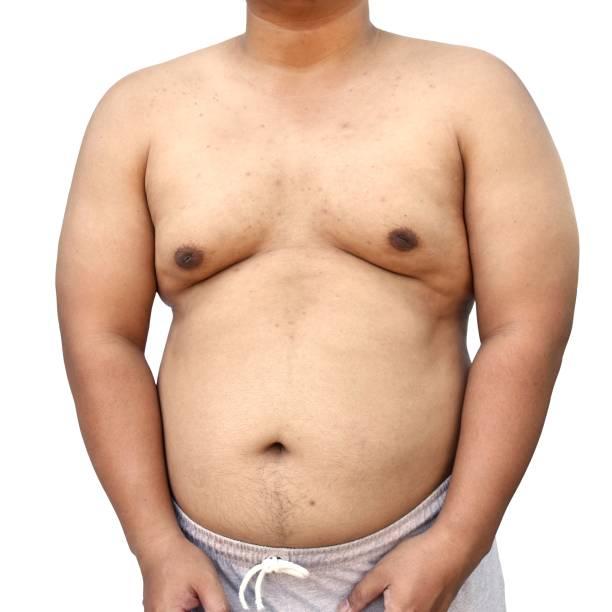
Gynecomastia, a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of male breast tissue, affects millions of men worldwide. It's often misunderstood, leading to embarrassment and self-consciousness for those experiencing it. This condition is not merely about excess fat in the chest area (which is called pseudogynecomastia); rather, it involves the actual glandular tissue of the breast. Understanding the nuances of gynecomastia is the first step toward seeking appropriate care and diagnosis, especially in a city like Riyadh where discretion and professional medical attention are highly valued.
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia results from an imbalance between the hormones estrogen and testosterone in the male body. While men naturally produce both hormones, an increase in estrogen levels relative to testosterone, or an increased sensitivity to estrogen, can lead to the growth of breast gland tissue. This hormonal shift can occur at various stages of life:
-
Infancy: Transient gynecomastia is common in newborn males due to maternal estrogen exposure.
-
Puberty: Adolescent boys often experience temporary gynecomastia as their hormones fluctuate. It usually resolves within a few months to a couple of years.
-
Adulthood: In older men, hormonal changes, certain medications, or underlying health conditions can trigger gynecomastia.
The condition can affect one or both breasts, and the enlargement can range from a subtle puffiness around the nipple to a more pronounced, breast-like appearance. Beyond the physical changes, gynecomastia can cause tenderness, pain, and significant psychological distress, impacting self-esteem and confidence.
Why is Accurate Diagnosis Crucial?
Accurate diagnosis is paramount for several reasons. Firstly, it differentiates true gynecomastia from pseudogynecomastia (excess fatty tissue) or, more importantly, from rare but serious conditions like male breast cancer. Secondly, identifying the underlying cause of gynecomastia guides the most effective treatment plan, which may range from watchful waiting and medication adjustments to surgical intervention.
The Diagnostic Journey for Gynecomastia in Riyadh
When a man in Riyadh experiences breast enlargement, seeking professional medical evaluation is a crucial step. Doctors in Gynecomastia in Riyadh employ a systematic diagnostic process to accurately identify the cause and type of breast enlargement. This comprehensive approach ensures that patients receive the most appropriate and effective care.
The Initial Consultation and Medical History
The diagnostic process typically begins with a thorough consultation with a healthcare professional, often a general practitioner, endocrinologist, or plastic surgeon specializing in male breast conditions. This initial meeting is vital for gathering key information.
-
Detailed Symptom History: The doctor will ask about the onset and duration of the breast enlargement, whether it affects one or both breasts, and if there is any associated pain, tenderness, or nipple discharge. They'll inquire about changes in breast size, consistency (firm or soft), and any lumps.
-
Medication Review: A comprehensive list of all current and past medications, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, anabolic steroids, and illicit substances, is essential. Many medications can cause gynecomastia as a side effect.
-
Medical History: Questions about pre-existing medical conditions (e.g., liver disease, kidney disease, thyroid disorders, hypogonadism, tumors), family history of gynecomastia or breast cancer, and any significant weight changes.
-
Lifestyle Factors: Discussion about alcohol consumption, drug use, and any significant changes in diet or exercise routines.
This detailed history helps the doctor narrow down potential causes even before a physical examination.
The Physical Examination: A Critical Step
A meticulous physical examination is a cornerstone of gynecomastia diagnosis. The doctor will assess the breast tissue, the surrounding areas, and other parts of the body that might offer clues about the underlying cause.
-
Breast Examination: The physician will gently palpate the breast tissue to differentiate between true glandular enlargement (which often feels firm, rubbery, and concentric with the nipple) and fatty tissue (which feels softer and is not necessarily centralized around the nipple). They will check for lumps, tenderness, and any skin changes or nipple discharge.
-
Nipple and Areola Assessment: Examining the nipples for any retraction, discharge, or changes in shape.
-
Abdominal and Testicular Examination: An examination of the abdomen may reveal signs of liver disease or tumors. A testicular examination is crucial to rule out testicular tumors, which can produce hormones that cause gynecomastia, or to assess testicular size for signs of hypogonadism.
-
Assessment for Other Signs: The doctor may also look for signs of other medical conditions, such as an enlarged thyroid (indicating thyroid issues) or signs of malnutrition.
This hands-on examination is often sufficient to make a preliminary diagnosis and guide further investigation.
Beyond the Physical: Laboratory and Imaging Tests for Diagnosis
While a thorough medical history and physical examination provide significant clues, doctors diagnosing Gynecomastia in Riyadh often rely on a range of laboratory and imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis, identify the specific cause, and rule out more serious conditions. These tests provide a deeper insight into the body's internal workings.
Blood Tests: Unveiling Hormonal Imbalances
Blood tests are fundamental in diagnosing gynecomastia, as hormonal imbalances are a primary cause. These tests measure the levels of various hormones and other substances in the blood:
-
Testosterone and Estrogen Levels: These are the most critical tests. An elevated estrogen-to-testosterone ratio is a common finding in true gynecomastia. Total testosterone, free testosterone, and estradiol (a potent form of estrogen) are usually measured.
-
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): These pituitary hormones regulate testosterone production in the testes. Abnormal levels can indicate primary testicular failure (high LH/FSH with low testosterone) or secondary hypogonadism (low LH/FSH with low testosterone, indicating a pituitary issue).
-
Prolactin (PRL): Elevated prolactin levels can sometimes cause breast enlargement and may indicate a pituitary tumor.
-
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG): High levels of hCG can be a sign of certain tumors (e.g., testicular germ cell tumors) that produce this hormone, leading to increased estrogen.
-
Thyroid Hormones (TSH, T3, T4): To check for hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), which can sometimes cause gynecomastia.
-
Liver and Kidney Function Tests: To assess the health of these organs, as liver or kidney dysfunction can affect hormone metabolism and lead to gynecomastia.
These blood tests help pinpoint specific hormonal or organ-related causes, guiding the next steps in treatment.
Imaging Tests: Visualizing the Breast Tissue
Imaging studies are often used to differentiate glandular tissue from fatty tissue and, crucially, to rule out male breast cancer, which, although rare, must always be considered.
-
Mammogram: This is a specialized X-ray of the breast and is often the primary imaging modality used. It can effectively distinguish between glandular tissue (characteristic of gynecomastia) and fatty tissue (pseudogynecomastia). It also helps identify suspicious masses that might indicate cancer.
-
Breast Ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to create detailed images of breast tissue. It's particularly useful for further evaluating any suspicious lumps found on physical examination or mammogram, and for differentiating between solid masses and cysts.
-
Testicular Ultrasound: If a testicular abnormality is suspected from the physical examination or blood tests (e.g., high hCG), a testicular ultrasound can help identify tumors or other issues in the testes.
-
CT Scans or MRI: In rare cases, if a pituitary or adrenal tumor is suspected based on hormone levels, a CT or MRI scan of those specific areas might be performed.
These imaging modalities provide crucial visual information, confirming the diagnosis and ensuring no serious underlying conditions are missed in the diagnosis of Gynecomastia in Riyadh.
The Role of Biopsy: When Further Investigation is Needed
In some instances, despite comprehensive blood tests and imaging, a definitive diagnosis remains elusive, or there's a lingering suspicion of malignancy. In such cases, a tissue biopsy becomes an essential diagnostic tool for Gynecomastia in Riyadh. While rare, male breast cancer can present similarly to gynecomastia, making biopsy a critical step in differential diagnosis.
What is a Biopsy?
A biopsy involves the removal of a small sample of breast tissue for microscopic examination by a pathologist. This is the only definitive way to confirm or rule out cancer.
-
Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy: A thin needle is used to extract cells from the suspicious area. It's less invasive but may not always provide enough tissue for a definitive diagnosis.
-
Core Needle Biopsy: A slightly larger, hollow needle is used to remove small cylinders of tissue. This provides more tissue for analysis than FNA.
-
Excisional Biopsy (Surgical Biopsy): In some cases, if the lump is significant or other biopsies are inconclusive, the entire suspicious mass may be surgically removed for examination. This is often the most definitive type of biopsy.
When is a Biopsy Recommended?
A biopsy is not routine for all cases of gynecomastia. It is typically recommended when:
-
Unilateral Enlargement: If only one breast is enlarged, especially if it feels firm, fixed, or irregular.
-
Rapid Growth: If the breast enlargement occurs very quickly.
-
Skin Changes: Presence of skin dimpling, redness, or ulceration.
-
Nipple Abnormalities: Nipple retraction, discharge (especially bloody), or changes in the nipple or areola.
-
Hard, Fixed Mass: A lump that feels hard, doesn't move easily, and is not concentric with the nipple.
-
Lymph Node Enlargement: Swollen lymph nodes in the armpit.
-
Age: While male breast cancer can occur at any age, the risk increases with age, making biopsy more likely in older men with suspicious findings.
-
Inconclusive Imaging: If mammogram and ultrasound findings are ambiguous and cannot definitively rule out malignancy.
The decision to perform a biopsy is made carefully by the healthcare team, weighing the patient's symptoms, physical exam findings, and imaging results. It serves as a vital safeguard to ensure that any potential malignancy is detected early and treated appropriately.
Differentiating True Gynecomastia from Pseudogynecomastia
A common challenge in diagnosing gynecomastia is distinguishing it from pseudogynecomastia, a condition where the male chest appears enlarged due to excess fat accumulation rather than glandular tissue growth. While both can cause cosmetic concerns, their underlying causes and treatment approaches differ significantly.
Understanding Pseudogynecomastia
Pseudogynecomastia, often seen in men who are overweight or obese, is characterized by the presence of fatty tissue in the breast area.
-
Feel of the Tissue: On physical examination, the tissue feels soft and fatty, lacking the firm, rubbery "disc" characteristic of glandular tissue. The fat is typically not concentric with the nipple.
-
Cause: Primarily due to generalized weight gain.
-
Treatment: Often responds to weight loss through diet and exercise. Liposuction is a common surgical solution to remove excess fat.
The Importance of Differentiation
Accurately differentiating between true gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia is crucial because:
-
Treatment Strategy: True gynecomastia may require hormonal management or glandular tissue excision, while pseudogynecomastia primarily responds to fat reduction techniques. A combined approach of liposuction and glandular excision is often used when both components are present.
-
Underlying Causes: True gynecomastia often points to hormonal imbalances or underlying medical conditions that need to be addressed. Pseudogynecomastia, while also indicating a need for lifestyle changes, doesn't typically suggest a specific hormonal issue.
-
Patient Expectations: Patients need to understand the nature of their condition to have realistic expectations about treatment outcomes.
The diagnostic process, particularly the physical examination and imaging, is designed to clearly distinguish between these two conditions, ensuring the patient receives the most appropriate and effective care for their specific situation.
The Journey to Treatment: What Happens After Diagnosis?
Once a clear diagnosis of Gynecomastia in Riyadh has been established and any underlying medical causes identified and addressed, the focus shifts to developing a personalized treatment plan. The approach depends heavily on the cause, the severity of the gynecomastia, and the patient's individual goals and preferences.
Watchful Waiting and Lifestyle Modifications
For many, especially adolescents with pubertal gynecomastia, a "wait-and-see" approach is often recommended, as the condition may resolve on its own as hormone levels stabilize.
-
Observation: Regular follow-up appointments to monitor the size and symptoms of the breast tissue.
-
Lifestyle Changes: For cases linked to obesity or certain lifestyle factors, weight loss through diet and exercise is encouraged. Avoiding substances known to contribute to gynecomastia (e.g., recreational drugs, excessive alcohol) is also crucial.
Medical Treatment
If hormonal imbalances are identified, or if the gynecomastia is persistent and bothersome, medical therapy might be considered.
-
Medication Adjustment: If a medication is identified as the cause, stopping or changing the medication (under medical supervision) can lead to resolution.
-
Hormonal Therapy: Medications like selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) such as tamoxifen or raloxifene, or aromatase inhibitors, may be prescribed to block estrogen's effects on breast tissue or reduce estrogen production. These are typically considered in specific cases, particularly if caught in the early stages, or to alleviate pain.
Surgical Intervention: Gynecomastia Surgery
When non-surgical treatments are ineffective, or for significant, long-standing gynecomastia that causes considerable distress, surgical correction is often the most definitive solution.
-
Liposuction: If the primary component is fatty tissue (pseudogynecomastia or mixed gynecomastia), liposuction can effectively remove the excess fat, creating a flatter chest contour.
-
Excision (Glandular Tissue Removal): For true glandular gynecomastia, or for cases with significant excess skin, surgical excision is performed. This involves making an incision (often around the edge of the areola) to remove the glandular tissue.
-
Combined Techniques: Many cases involve both excess fat and glandular tissue, requiring a combination of liposuction and excision for optimal results.
-
Skin Resection: In severe cases with significant skin laxity (often after massive weight loss), skin may also need to be removed to achieve a taut, masculine chest contour.
The decision for surgery is a collaborative one between the patient and a qualified plastic surgeon, taking into account the patient's overall health, the extent of the gynecomastia, and their aesthetic goals. The aim is to create a more masculine chest contour, significantly improving confidence and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Navigating a diagnosis for gynecomastia can bring up many questions. Here are some commonly asked ones, uniquely addressed to provide clear and helpful insights.
Many Wonder: How can I tell if my breast enlargement is true gynecomastia or just fat?
Differentiating between true gynecomastia (glandular tissue) and pseudogynecomastia (fatty tissue) is a common concern. You can often do a simple self-check: lie flat on your back and gently pinch the tissue around your nipple between your thumb and forefinger. If you feel a firm, rubbery disc-like mass, especially concentrated directly behind the nipple, it's more likely true glandular gynecomastia. If it feels soft and rolls easily, like the fat elsewhere on your body, it's more likely pseudogynecomastia. However, a definitive diagnosis requires examination by a doctor in Riyadh who can accurately assess the tissue and may order further tests.
Often Asked: Do I always need blood tests for a gynecomastia diagnosis in Riyadh?
While not always strictly necessary in every case (for example, clear-cut pubertal gynecomastia that is expected to resolve), blood tests are highly recommended and frequently performed during a comprehensive gynecomastia diagnosis in Riyadh. They are crucial for identifying underlying hormonal imbalances (like low testosterone or high estrogen) or other medical conditions (such as thyroid, liver, or kidney issues) that could be causing the breast enlargement. These tests ensure that the root cause is understood, allowing for the most appropriate and effective treatment plan, whether it's medical management or surgical consideration.
People Also Ask: Can male breast cancer be mistaken for gynecomastia?
Yes, male breast cancer can sometimes be mistaken for gynecomastia, which is why a thorough and professional diagnosis is so critical. While male breast cancer is rare, its symptoms can overlap with gynecomastia, such as a lump in the breast area. However, male breast cancer typically presents as a hard, firm, fixed lump, often located off-center from the nipple, and may be accompanied by skin changes, nipple retraction, or discharge from one nipple. Any unilateral (one-sided) breast enlargement, particularly if it feels suspicious or is accompanied by these other symptoms, warrants immediate medical evaluation, including imaging tests like a mammogram and potentially a biopsy, to definitively rule out cancer.
Frequently Inquired: If I have gynecomastia, will I definitely need surgery?
Not necessarily. The need for surgery depends on the specific cause, the severity of the condition, and your personal concerns. For adolescent gynecomastia, a "wait-and-see" approach is common as it often resolves naturally. If an underlying medical condition or medication is the cause, treating that condition or adjusting the medication may lead to resolution. Medical therapies might also be considered for certain hormonal imbalances. Surgery, which involves removing glandular tissue and/or fat, is generally recommended for persistent, bothersome gynecomastia that hasn't responded to other treatments, or for significant enlargement that causes considerable psychological distress. Your doctor will discuss all available options to find the best approach for you.
If you are experiencing concerns about male breast enlargement and seeking expert advice in Riyadh, take the proactive step towards understanding your condition and exploring effective solutions. We invite you to schedule a confidential consultation with the specialists at Royal Clinic Saudia.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Startseite
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Andere
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


