Environmental and Regulatory Aspects of Hydrazine Hydrate Market
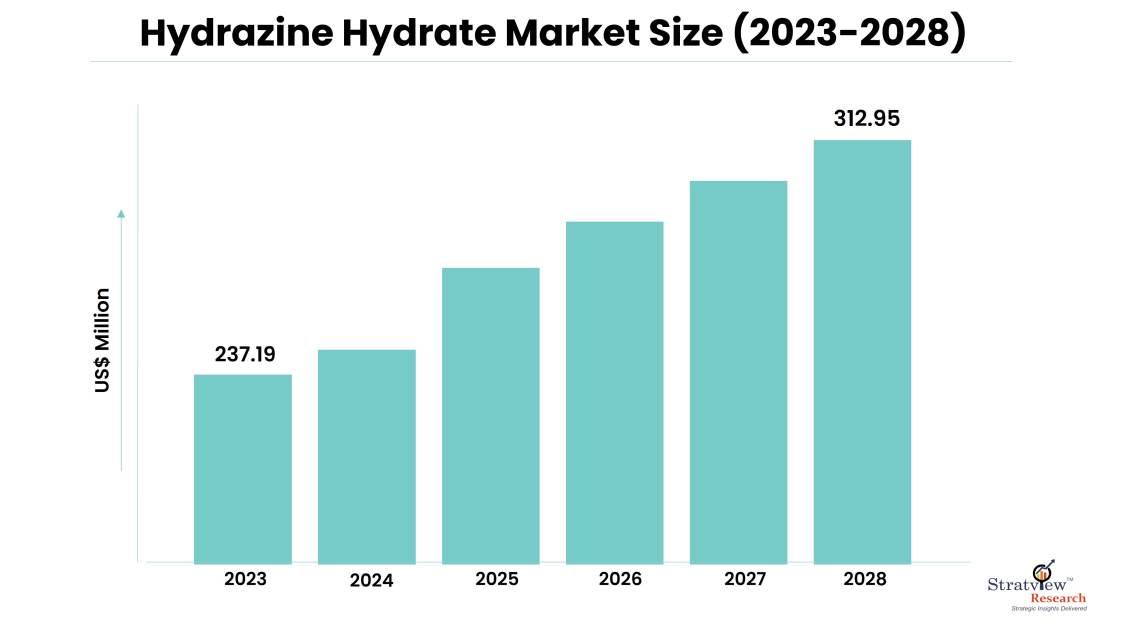
The hydrazine hydrate market, driven by its numerous industrial applications, has been under increasing scrutiny from environmental and regulatory perspectives. This versatile chemical compound, with the formula N2H4·H2O, is widely used in sectors such as aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment. While its utility cannot be denied, concerns regarding its environmental impact and strict regulations have become paramount in shaping the industry's future. The hydrazine hydrate market is estimated to grow from USD 237.19 million in 2023 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 5.70% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 312.95 million by 2028.
Environmental Concerns:
Hydrazine hydrate, despite its versatility, is not without environmental drawbacks. Here are some of the key environmental concerns associated with its production and usage:
Toxicity: Hydrazine hydrate is highly toxic to humans and aquatic life. Accidental spills or improper disposal can lead to serious environmental contamination and pose health hazards to workers and nearby communities.
Air Pollution: The combustion of hydrazine hydrate produces nitrogen oxides (NOx), which contribute to air pollution and have adverse effects on air quality and human health. This is particularly concerning in the aerospace industry, where hydrazine is used as rocket fuel.
Persistence in the Environment: Hydrazine hydrate can persist in the environment for an extended period, leading to long-term contamination of soil and water. This persistence can be detrimental to ecosystems.
Safety Hazards: Handling and storing hydrazine hydrate require strict safety measures due to its flammability and potential for explosive reactions. Accidents involving this chemical can lead to significant environmental damage.
Regulatory Framework:
To mitigate these environmental concerns and ensure the safe handling and use of hydrazine hydrate, various regulatory bodies have established stringent regulations and guidelines. These regulations primarily focus on safety, transportation, and environmental protection. Here are some of the key aspects of the regulatory framework for hydrazine hydrate:
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): OSHA in the United States has established regulations governing the safe handling of hydrazine hydrate in the workplace. These regulations include guidelines on personal protective equipment (PPE), hazard communication, and emergency response procedures.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): The EPA regulates the environmental aspects of hydrazine hydrate use and disposal. This includes guidelines for managing spills, reporting releases, and ensuring safe storage and transportation.
Transportation Regulations: Transporting hydrazine hydrate is subject to strict regulations outlined by various transportation authorities. The United Nations, through its Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, provides guidelines for the safe transportation of hydrazine hydrate and other hazardous chemicals.
International Regulations: Since hydrazine hydrate is used in the aerospace industry, it is subject to international regulations, including those set by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the European Space Agency (ESA). These regulations ensure the safe handling and transportation of hydrazine on a global scale.
Environmental Mitigation and Future Trends:
Given the environmental concerns associated with hydrazine hydrate, the industry is actively exploring ways to mitigate its impact and develop cleaner, more sustainable production methods. Some of the trends and developments in this regard include:
Alternative Propellants: In the aerospace industry, there is ongoing research into alternative propulsion systems that are less harmful to the environment than traditional hydrazine-based systems. Green propulsion technologies aim to reduce the emissions associated with rocket launches.
Safer Production Methods: Manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve the safety and environmental sustainability of hydrazine hydrate production processes. This includes efforts to reduce waste and emissions.
Environmental Monitoring: Environmental monitoring systems and technologies are being implemented to detect and mitigate the environmental impact of hydrazine hydrate usage. This includes real-time monitoring of air and water quality in and around industrial facilities.
In conclusion, while hydrazine hydrate continues to be a valuable chemical compound with a wide range of industrial applications, environmental concerns and strict regulations are shaping the way it is produced, handled, and used. The industry's commitment to safety and sustainability, along with ongoing research into cleaner alternatives, will play a crucial role in addressing these concerns and ensuring a more environmentally responsible hydrazine hydrate market in the future.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Startseite
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Andere
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


