Fiber Reinforced Concrete: The Future of Construction Material
Concrete is undoubtedly the most widely used construction material across the globe. However, traditional concrete has some key limitations like low tensile strength and cracking.
What is Fiber Reinforced Concrete?
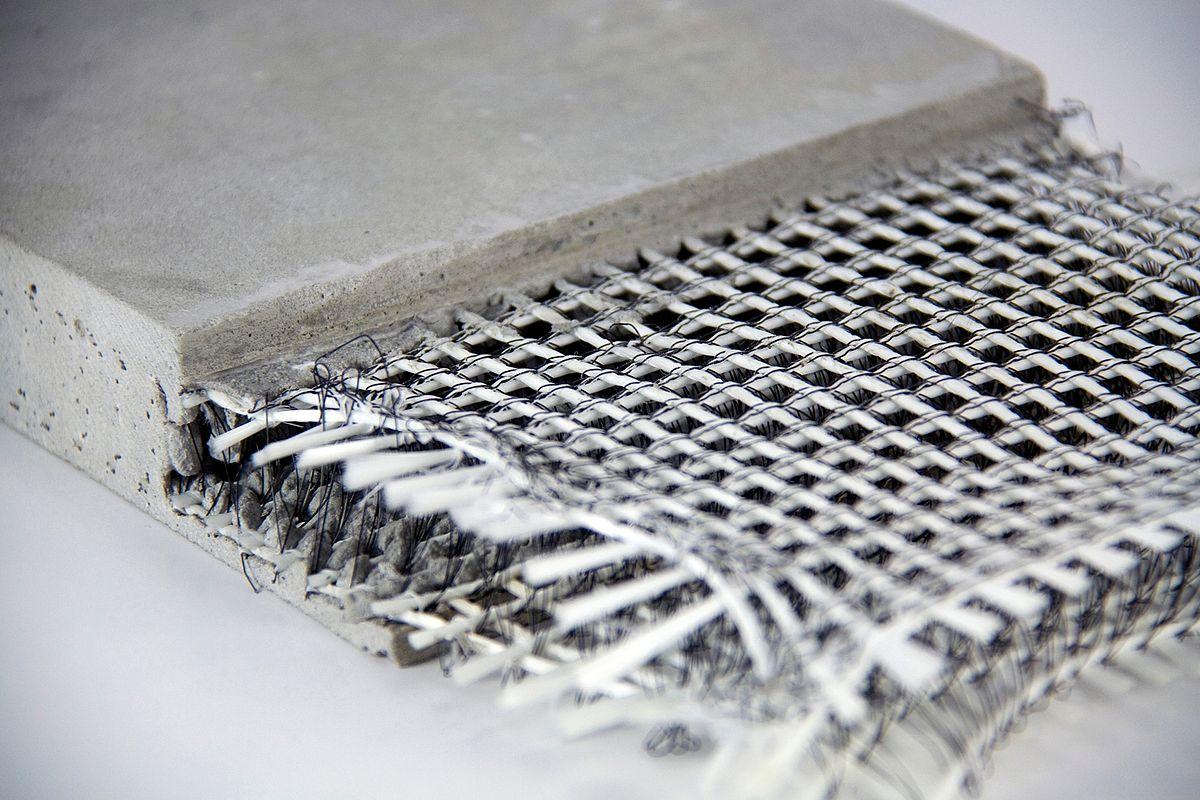
Fiber reinforced concrete (FRC) is a concrete containing fibrous material which increases its structural integrity. Fibrillated fibers are added to the concrete mixture before it sets, resulting in a composite material that resists cracking and has significantly higher tensile strength compared to plain concrete. The fibers incorporated into the concrete matrix range from 1⁄2 to 2 inches in length. Some common fiber materials used include steel, glass, carbon and synthetic fibers. When fibers are added to concrete mix, it helps in controlling cracks and provides reinforcement at the microscopic level.
Types of Fibers Used
Depending on the material used, there are different types of fiber reinforced concrete:
- Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete: Steel fibers are most commonly used fibers due to their high tensile strength. They can increase flexural strength up to 6 times and impact resistance up to 20 times compared to plain concrete. However, corrosion is a major issue.
- Synthetic Fiber Reinforced Concrete: Synthetic fibers like polypropylene and nylon fibers are recognized for their high durability and corrosion resistance. They add tensile strength, control shrinkage cracks but provide lower reinforcement compared to steel fibers.
- Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete: Glass fibers have high tensile strength and young's modulus but are less ductile than steel and synthetic fibers. They are susceptible to alkaline attack in concrete resulting in loss of physical properties over time.
- Carbon Fiber Reinforced Concrete: Carbon fibers have very high tensile strength and modulus of elasticity providing excellent reinforcement. However, their use is limited due to very high costs.
Advantages of Fiber Reinforced Concrete
Increased Tensile Strength and Ductility
Plain concrete is weak in tension and brittle in nature. Fibers in concrete enhance the ability to resists cracking and increase both tensile strength and ductility manifold. The addition of short discrete fibers creates multiple crack arrest points when a crack forms and thus improves toughness.
Reduced Permeability and Increased Durability
The closely spaced fibers in concrete help in filling up the voids and micro-cracks. This refinement of pores results in low permeability and less penetration of chlorides, water and other agents that cause corrosion and decay. Thus, fiber reinforced concrete structures last longer.
Improved Impact and Shrinkage Cracking Resistance
Fibers improve the ability of concrete to absorb higher energy under impact loads and dynamic forces. They control shrinkage cracking during concrete drying and help in bridging shrinkage cracks.
Applications of Fiber Reinforced Concrete
Some major applications where fiber reinforced concrete is increasingly being used are:
- Industrial Flooring Systems - Used in warehouses, parking garages, hangars etc. where impact and shrinkage cracking resistance is important.
- Overlays and Repair Mortars - Excellent for repairing worn surfaces, cracks and adding an overlay to strengthen existing structures.
- Thin Concrete Elements - Can be used to cast thin slabs, precast elements and lightweight structural components.
- Shotcrete - Suitable for rock stabilization, tunnel linings where sprayed on wet concrete method is adopted.
- Concrete Masonry Units - Helps in controlling cracking in concrete blocks used in construction.
- High-Performance Concrete - Used where mechanical properties, resistance to environment is critical like marine structures.
Explore Our More Blogs Here: https://www.newsanalyticspro.com/fibercraft-reinventing-concrete-with-strength-and-flexibility/
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Игры
- Gardening
- Health
- Главная
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Другое
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


