Unleashing the Power of Passive Optical LAN: A Future-Ready Blueprint for Scalable and Cost-Effective Connectivity
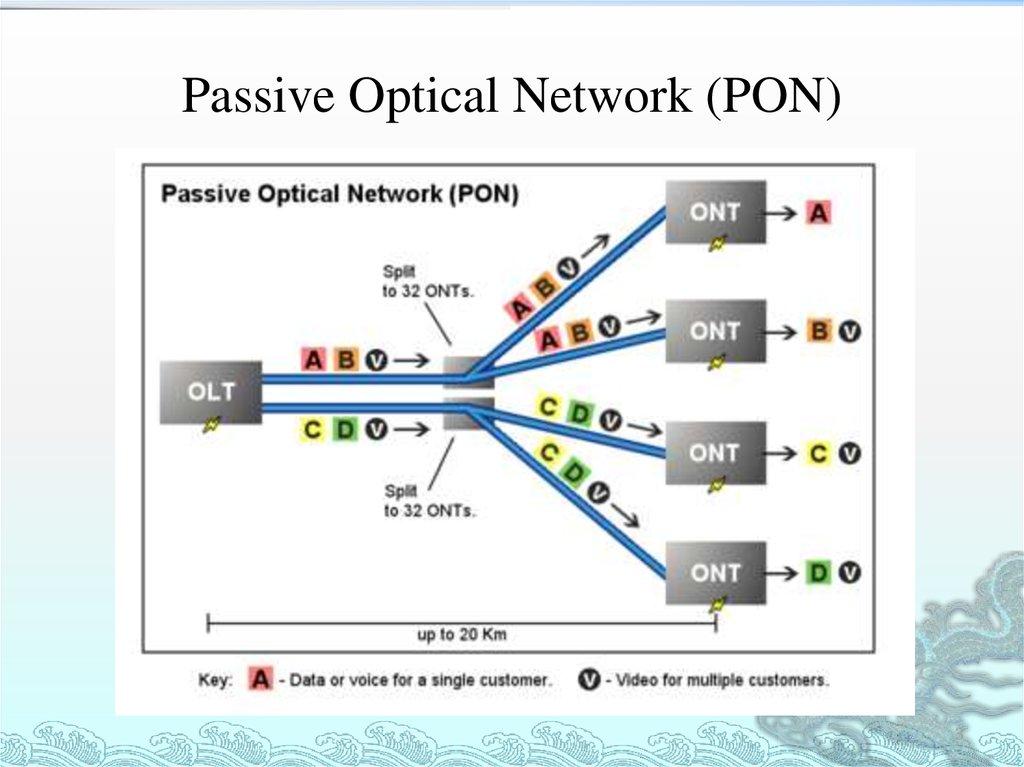
Passive Optical LAN or POL is an emerging fiber optic connectivity technology that is revolutionizing how businesses and organizations connect their infrastructure and deliver bandwidth intensive services. A POL uses point-to-multipoint fiber architecture to deliver broadband communication and networking capabilities without any active electronic components present in the transmission path of the optical signal. This article will discuss key aspects of POL technology, its architecture, components, advantages and applications in enterprise networking.
POL Architecture
A typical POL architecture consists of an Optical Line Terminal (OLT) located at the provider's central office or point of presence. The OLT acts as a media converter, connecting the provider's metro network to the local access network. From the OLT, a fiber cable runs to a series of passive splitters placed throughout the campus or workplace. These passive splitters divide the optical signal from the OLT and send it to multiple Optical Network Terminals (ONTs) via separate strands of fiber. Each ONT then provides network access to individual desktops, wireless access points, IP cameras or other end devices through either copper or wireless connectivity. This point-to-multipoint architecture allows a single fiber from the OLT to deliver bandwidth to multiple ONTs using wavelength division multiplexing technology without any active electronic components in the field.
Components of a POL
The main components required to build a POL are the OLT, optical splitters and ONTs.
- OLT: As mentioned earlier, the OLT is placed at the central office and acts as the network gateway. It aggregates traffic from the metro network and uses laser transmitters to send optical signals through the fiber.
- Optical Splitters: These passive components split the optical signals from the OLT and transmit them to multiple ONTs without any power or active electronics involved. Typical split ratios range from 1:4 to 1:32.
- ONTs: Each network device like a desktop or access point connects to the network through an ONT installed on-premise. ONTs use optical receivers to receive signals from the field fiber and convert them into electrical signals for client devices using Ethernet or other connectivity types.
Advantages of POL over Copper
Some key advantages that POL offers over traditional copper-based Ethernet or WiFi networks for enterprise connectivity are:
Higher Bandwidths: POL networks utilize the vastly larger bandwidth capabilities of optical fiber to support high speed connectivity up to 10Gbps or more to desktops compared to traditional copper's limitation of 1Gbps. This futureproofs the network for bandwidth intensive applications.
Lower Cost of Ownership: Once installed, a Passive Optical LAN network has very low operating costs since it has no active equipment in the field. Troubleshooting and maintenance costs are also much lower than managing active Ethernet switches distributed across buildings.
Future Scalability: Additional bandwidth can be provisioned by upgrading the OLT's capabilities. New desktops, wireless access points or servers can also be easily added by installing new low-cost ONTs without upgrading the entire infrastructure.
Unified Wireless and Wired Connectivity: With WiFi capabilities in ONTs, POL provides a single integrated network solution to deliver both wired and wireless services campus-wide.
Reliability: As there are no active field components, POL networks experience fewer failures and outages compared to networks with distributed electronics in the wiring closets.
Applications of POL
Some popular use cases where organizations are leveraging POL include:
- University/School Campus Networks: To deliver multi-gigabit bandwidth uniformly across a campus for supporting 8K video, VR labs and IoT networks.
- Healthcare Facilities: To interconnect various telehealth applications, imaging systems, nursing workstations with high reliability.
- Enterprises: For connecting offices across multiple buildings with a futureproofed 10Gbps capable infrastructure for big data and cloud applications.
- Hotels, Convention Centers: To deliver consistent high-speed connectivity in guest rooms and meeting spaces with minimum wiring.
- Surveillance: To transport multiple high resolution video streams from IP cameras back to a central NVR over a single fiber.
POL technology is revolutionizing enterprise networking by delivering multi-gigabit bandwidth capabilities using a simple yet robust point-to-multipoint fiber architecture. With its lower upfront and operating costs, easy scalability, unified wired and wireless services - POL is becoming the connectivity infrastructure of choice for both new and upgraded commercial deployments. As bandwidth demands increase exponentially, POL will continue playing a strategic role in transforming how organizations interconnect their distributed sites and resources with maximum efficiency.
For More details on the topic:
https://www.insightprobing.com/passive-optical-lan-the-future-of-network-infrastructure/
Check more trending articles related to this topic:
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Игры
- Gardening
- Health
- Главная
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Другое
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


