Ethyl Acetate in Focus: Exploring Its Chemical Composition and Uses
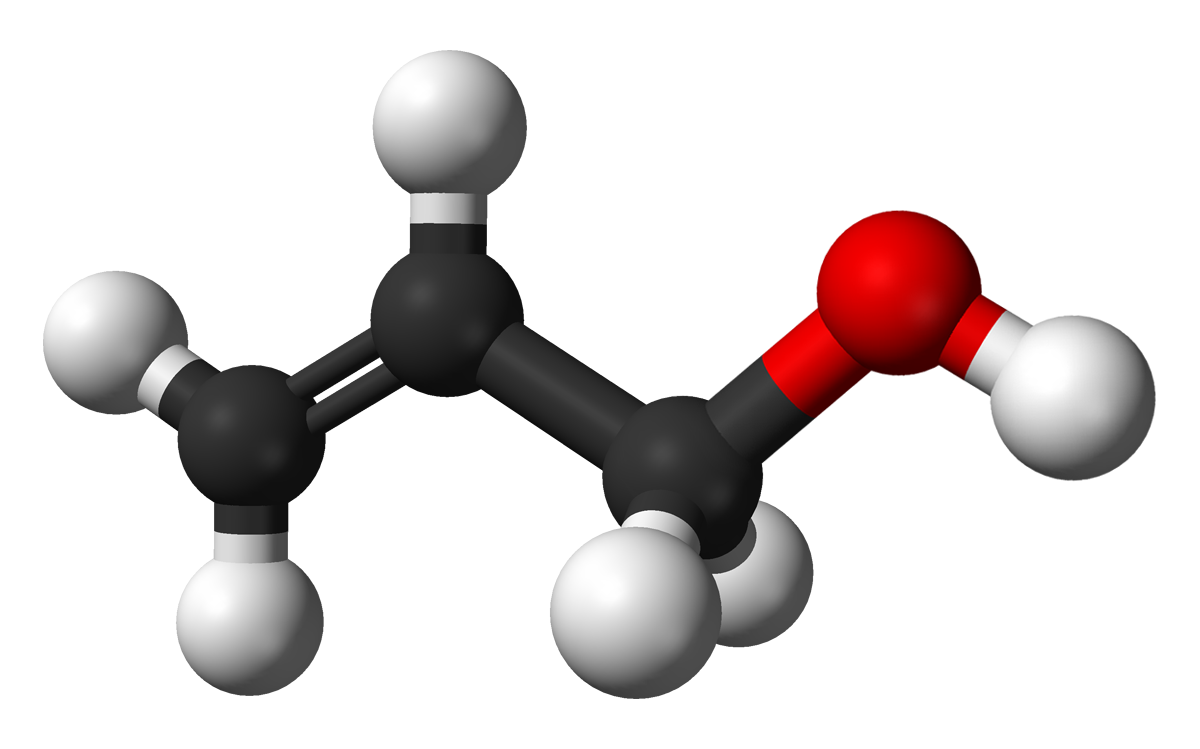
Ethyl acetate is an organic compound that has a wide range of applications in chemical and allied industries due to its pleasant smell and safe toxicity profile. In this article, we will explore the various properties and uses of ethyl acetate along with discussing its production methods and regulations.
Chemical Properties
Ethyl acetate has the chemical formula C4H8O2. It is a colorless, volatile liquid with a characteristic pleasant, fruity odor. Its molecular weight is 88.11 g/mol and boiling point is 77.1°C. Ethyl acetate is soluble in water as well as organic solvents like ethanol, ether, acetone etc. However, it is hygroscopic in nature and absorbs moisture from air over time. Its refractive index is 1.37 and vapor density is 2.0.
Production
Ethyl acetate is commercially produced via two major chemical processes - direct esterification and transesterification. In direct esterification, acetic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst like sulfuric or phosphoric acid. This reversible reaction produces ethyl acetate and water as byproducts. Transesterification involves reacting ethanol with vinyl acetate monomer in the presence of a basic catalyst like sodium or potassium ethylate to shift the equilibrium towards product formation. Modern plants use sophisticated reactors and distillation columns for high yield production of ethyl acetate.
Uses and Applications
Ethyl acetate finds widespread applications in pharmaceuticals, food flavors, cosmetics, paints, coatings and more due to its pleasant smell and safe toxicity profile. Some major uses are:
- Solvent in production of coatings and paints: It is used as a thinner and solvent for lacquers, varnishes and paints due to its fast evaporation rate.
- Pharmaceutical applications: It acts as a carrier for active pharmaceutical ingredients and flavors which are encapsulated or added to tablet coatings.
- Food flavors and extracts: Ethyl acetate is approved as a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) substance for direct food contact. It extracts essential oils from plants and tobacco to produce natural flavors.
- Nail polish removers: The fast evaporation and mild smell of ethyl acetate makes it suitable for formulating nail polish removers.
- Adhesives and glues: It dissolves various resins used in manufacture of adhesives, glues and contact cements.
- Printing inks: Ethyl acetate is used as a solvent in flexographic and lithographic printing inks.
- Photography film developer: Previously it was used as a developer solvent in photography films.
Safety and Regulations
Ethyl Acetate has relatively low oral toxicity with an LD50 dose of 5620 mg/kg in rats. However, it can cause irritation to eyes and respiratory tract when inhaled in high doses. The occupational exposure limits set by organizations like NIOSH and ACGIH are 400-1400 mg/m3. Being flammable, it requires careful handling and storage away from ignition sources. Ethyl acetate is listed on the EPA's list of 302 extremely hazardous substances. Its use and disposal are regulated under various environmental laws. The FDA has approved it as a direct and indirect food additive. Overall, with proper safety measures, it provides a efficient and cost-effective solvent option for industries.
With a global production capacity of over 3.2 million tons annually and approval for direct food contact, it has become an integral part of many industries. As environmental regulations tighten, industry is continuously working towards developing cleaner and more sustainable production processes for this important industrial chemical.
Get more insights on this topic: https://www.newsanalyticspro.com/ethyl-acetate-unveiled-from-formulation-to-function/
Explore more information on this topic, Please visit: https://captionssky.com/solar-panel-automatic-cleaning-robot-the-future-of-solar-energy-production/
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jocuri
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Alte
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


