The Visionary World of Microdisplay Market Shaping the Future of Visual Technologies
Introduction
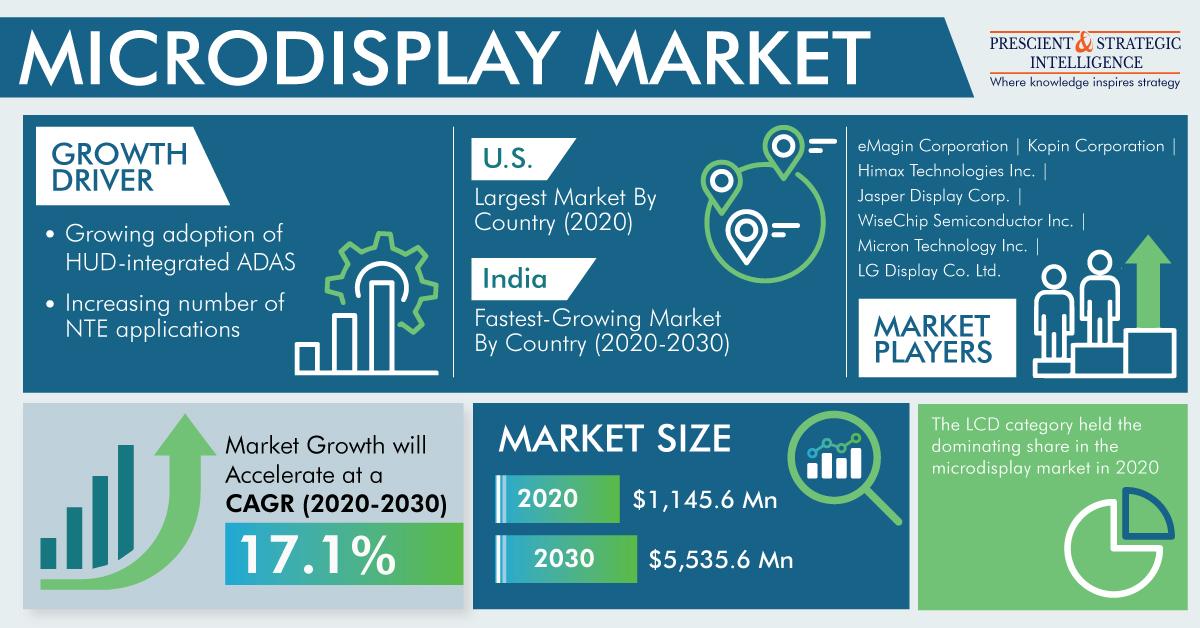
The microdisplay market, characterized by its compact size and high-resolution displays, is revolutionizing the way we perceive and interact with visual information. From augmented reality (AR) headsets to heads-up displays (HUDs) in automobiles, microdisplays are driving innovation across a diverse range of industries, offering immersive viewing experiences, enhanced portability, and unparalleled image quality. This article delves into the dynamic landscape of the microdisplay market, uncovering key trends, applications, and growth drivers shaping its trajectory.
Unveiling the Dynamics: Understanding Microdisplay Technology
OLED Microdisplays
Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) microdisplays are at the forefront of display technology, offering vibrant colors, deep blacks, and excellent contrast ratios in a compact form factor. With self-emissive pixels and high refresh rates, OLED microdisplays deliver stunning visual experiences ideal for virtual reality (VR), gaming, and wearable devices.
LCoS Microdisplays
Liquid Crystal on Silicon (LCoS) microdisplays utilize liquid crystal technology integrated onto a silicon backplane to produce high-resolution images with exceptional brightness and clarity. LCoS microdisplays are widely used in head-mounted displays (HMDs), head-up displays (HUDs), and electronic viewfinders (EVFs) for cameras, offering superior performance in various lighting conditions.
Driving Innovation: Applications Across Industries
Consumer Electronics
In the realm of consumer electronics, microdisplays power a myriad of devices, including smart glasses, digital cameras, and wearable fitness trackers. From immersive gaming experiences to real-time health monitoring, microdisplays enhance the functionality and user experience of electronic devices, driving demand and innovation in the consumer electronics market.
Automotive
In the automotive sector, microdisplays play a vital role in enhancing driver safety, convenience, and entertainment. Heads-up displays (HUDs) project critical information, such as speed, navigation directions, and collision warnings, onto the windshield, minimizing distractions and improving situational awareness for drivers.
Overcoming Challenges: Addressing Technological Barriers and Market Constraints
Cost Constraints
Despite technological advancements, the high manufacturing costs associated with microdisplay fabrication remain a significant barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in cost-sensitive consumer markets. However, ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving production processes and economies of scale are expected to drive down costs and expand market accessibility in the coming years.
Technological Limitations
While microdisplay technology offers numerous benefits, including high resolution, compact size, and energy efficiency, it also faces challenges such as limited field of view, pixel visibility, and image persistence. Addressing these technological limitations requires ongoing innovation in display materials, optics, and image processing algorithms to deliver seamless and immersive visual experiences.
Exploring Opportunities: Future Trends and Market Projections
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
The proliferation of AR and VR applications across industries, including gaming, education, healthcare, and enterprise, presents immense opportunities for microdisplay technology. As AR and VR experiences become increasingly integrated into everyday life, the demand for high-performance microdisplays capable of delivering immersive and realistic visuals is expected to surge, driving market growth and innovation.
Healthcare and Medical Devices
In the healthcare sector, microdisplays are revolutionizing medical imaging, surgical visualization, and patient monitoring applications. From augmented reality surgical navigation systems to wearable health monitoring devices, microdisplay technology enables healthcare professionals to access critical information in real time, enhance diagnostic accuracy, and improve patient outcomes.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How do microdisplays differ from traditional displays?
Microdisplays are compact, high-resolution display panels typically used in applications requiring miniaturized visual displays, such as AR/VR headsets, heads-up displays (HUDs), and wearable devices, whereas traditional displays are larger, bulkier screens commonly found in televisions, computer monitors, and smartphones.
What are the advantages of OLED microdisplays?
OLED microdisplays offer vibrant colors, deep blacks, and high contrast ratios, thanks to their self-emissive pixel technology, making them ideal for applications requiring superior image quality and color accuracy, such as virtual reality (VR) headsets and digital cameras.
How are microdisplays used in automotive applications?
Microdisplays are integrated into heads-up displays (HUDs) in automobiles to project critical information, such as speed, navigation directions, and vehicle warnings, onto the windshield, allowing drivers to access important information without taking their eyes off the road.
What challenges does the microdisplay market face?
The microdisplay market faces challenges such as high manufacturing costs, technological limitations, and competition from alternative display technologies, requiring ongoing innovation and investment to overcome these barriers and drive market growth.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


