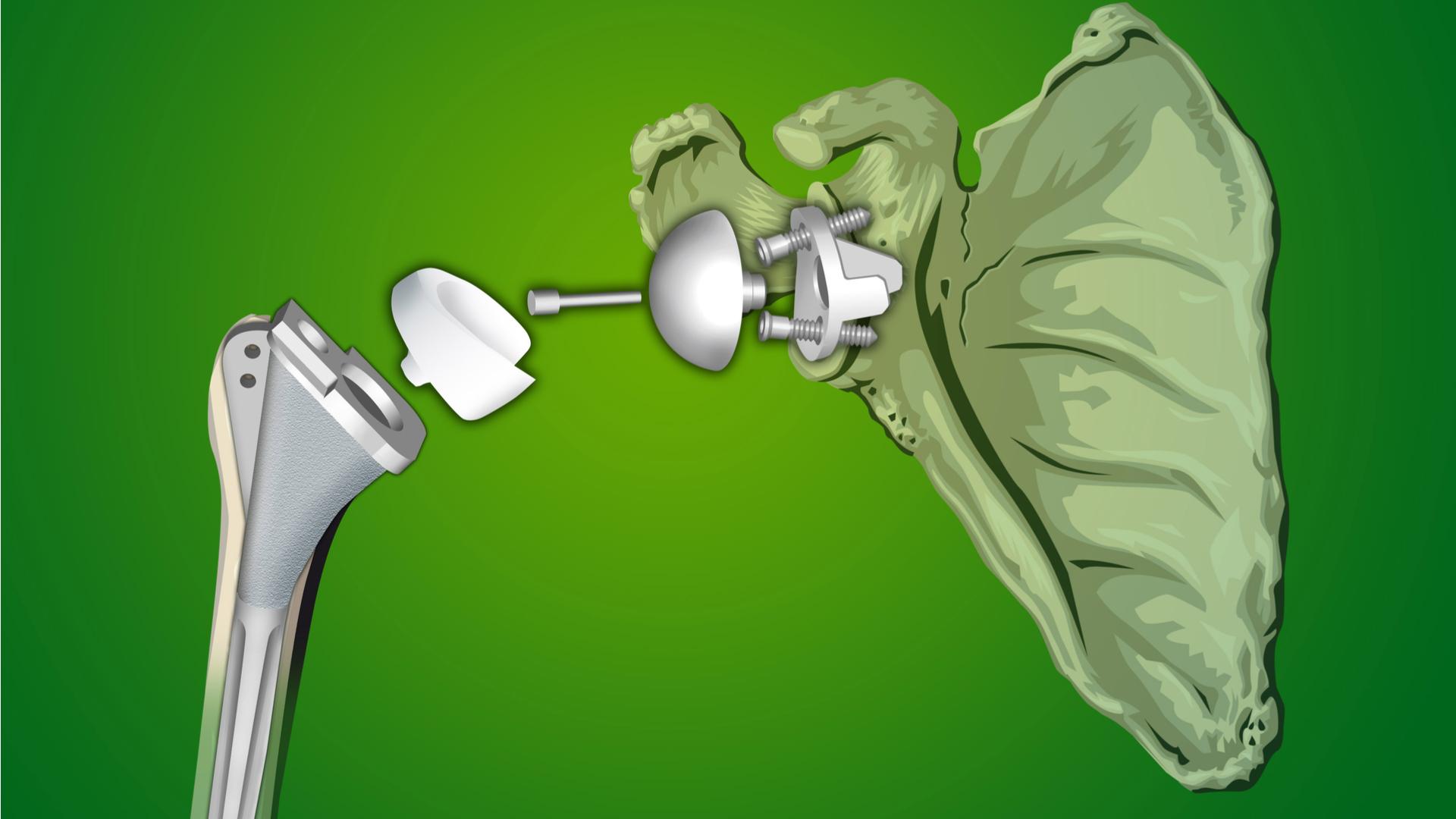
What is an Endoprosthesis?
An endopolyploidy, commonly known as an implant, is a medical device that is placed inside the body to replace a missing biological structure like a joint or bone. It is used in joint replacement surgeries like hip replacement, knee replacement, and shoulder replacement to replace the damaged bone and cartilage.
Knee Replacement Endoprosthesis
One of the most common joint replacement procedures is knee replacement surgery which uses a knee Endoprosthesis. The knee endopolyploidy consists of three parts - two metal plates that replace the surface of the thigh bone (femur) and shin bone (tibia), and a plastic spacer that fits between the metal plates. The surgery involves removing the damaged surfaces of the femur and tibia and replacing them with the metal prosthesis parts. The plastic spacer acts as a buffer between the metal parts and helps smoothen their joint movement. A knee endopolyploidy aims to reduce pain and improve mobility by replacing the damaged knee joint.
Hip Replacement Endopolyploidy
Hip replacement surgery is another widely performed procedure that replaces the hip joint using a hip endopolyploidy. The hip endopolyploidy has three main parts - a stem inserted into the femur, a ball that replaces the femoral head, and a cup inserted into the pelvis. During surgery, the damaged femoral head and neck are cut off and replaced with the ball and stem components. The plastic or metal cup replaces the damaged or worn out socket surface in the pelvis. The goal of hip replacement using an endopolyploidy is to relieve pain and restore mobility in patients with severe hip arthritis or fracture.
Get More Insights on- Endoprosthesis