"From Grain to Gain: Blockchain’s Impact on Agriculture and Food Chains"
Introduction
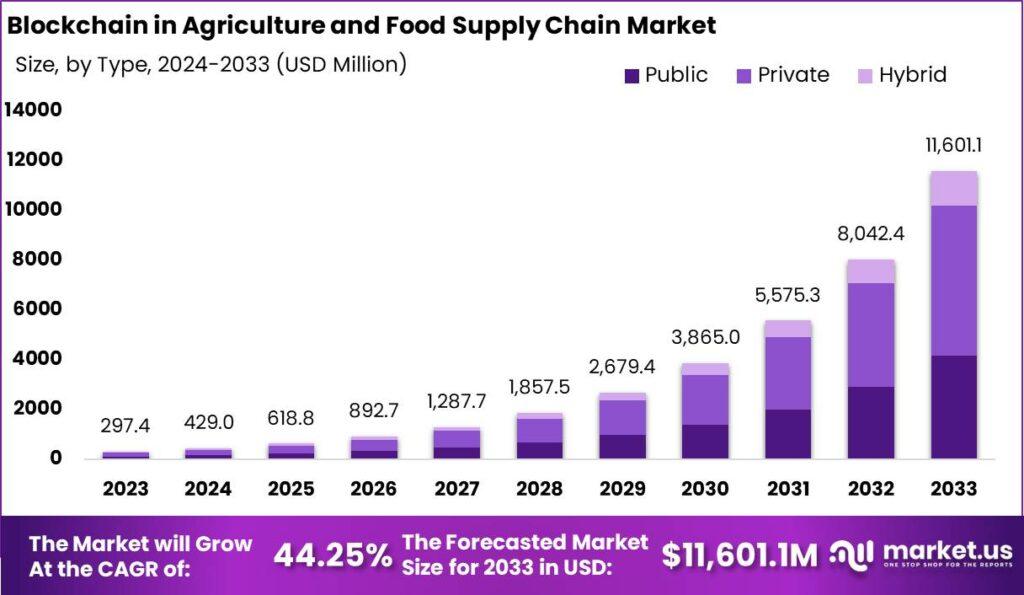
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the agriculture and food supply chain market by providing transparency, traceability, and efficiency. As consumer demand for food safety and sustainability increases, the need for reliable, transparent systems has become paramount. Blockchain’s ability to create a secure, decentralized ledger makes it a perfect fit for the agriculture sector, where it can ensure the authenticity of products, track their journey from farm to table, and reduce fraud.
Read More - https://market.us/report/blockchain-in-agriculture-and-food-supply-chain-market/
However, despite its promising growth, the blockchain in agriculture faces challenges such as high implementation costs, lack of standardization, and the need for widespread industry adoption. For new entrants, these challenges can be daunting, but they also present opportunities. By addressing these challenges with innovative solutions, new players can carve out a niche in this growing market.
Emerging Trends
- Smart Contracts: Automating processes like payments, deliveries, and quality checks.
- Food Traceability: Blockchain ensures the tracking of food products from origin to consumer, enhancing safety and reducing fraud.
- Sustainability Tracking: Blockchain helps in monitoring sustainable farming practices, ensuring environmental standards are met.
- Decentralized Marketplaces: Farmers and producers can connect directly with consumers, cutting out intermediaries.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Blockchain facilitates the collection and analysis of vast amounts of data, improving agricultural productivity.
Top Use Cases
- Supply Chain Transparency: Ensuring every step in the food supply chain is recorded and visible, from farm to fork.
- Food Safety: Identifying and removing contaminated products quickly, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
- Fair Trade Practices: Ensuring that farmers receive fair payment for their products by eliminating middlemen.
- Reduction of Food Waste: By providing real-time data, blockchain helps in better inventory management, reducing spoilage and waste.
- Organic Certification: Authenticating organic products to prevent fraud and ensure compliance with organic standards.
Major Challenges
- High Implementation Costs: Setting up blockchain infrastructure can be expensive, particularly for small farmers and companies.
- Lack of Standardization: Different blockchain platforms can lead to compatibility issues, making it hard to create a unified system.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Storing sensitive information on a blockchain raises concerns about data security and privacy.
- Technical Complexity: The complexity of blockchain technology requires specialized knowledge, which may not be readily available in the agricultural sector.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Governments are still grappling with how to regulate blockchain technology, creating uncertainty for companies.
Market Opportunity
- Improving Food Safety: With rising consumer concerns over food safety, blockchain offers a unique solution to ensure the quality and safety of food products.
- Enhancing Supply Chain Efficiency: Blockchain can significantly reduce inefficiencies in the supply chain, saving time and money.
- Meeting Consumer Demand for Transparency: As consumers become more concerned with where their food comes from, blockchain provides a way to meet this demand.
- Supporting Sustainable Practices: Blockchain can be used to track and verify sustainable farming practices, meeting the growing demand for environmentally friendly products.
- Accessing New Markets: By ensuring product authenticity, blockchain can open up new markets for organic and specialty products, particularly in regions where food fraud is a concern.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is set to play a transformative role in the agriculture and food supply chain market, addressing key issues such as transparency, traceability, and sustainability. While the road to widespread adoption is not without its challenges, the potential benefits far outweigh the hurdles. For new entrants, the market offers significant opportunities, particularly in areas like food safety, supply chain efficiency, and consumer transparency.
By leveraging blockchain technology, companies can not only improve their operations but also gain a competitive edge in an increasingly complex and demanding marketplace. As the technology matures, it is likely to become an essential tool for ensuring the integrity and efficiency of the global food supply chain.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Giochi
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Altre informazioni
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


