Market Dynamics Influencing the Machine Safety Industry
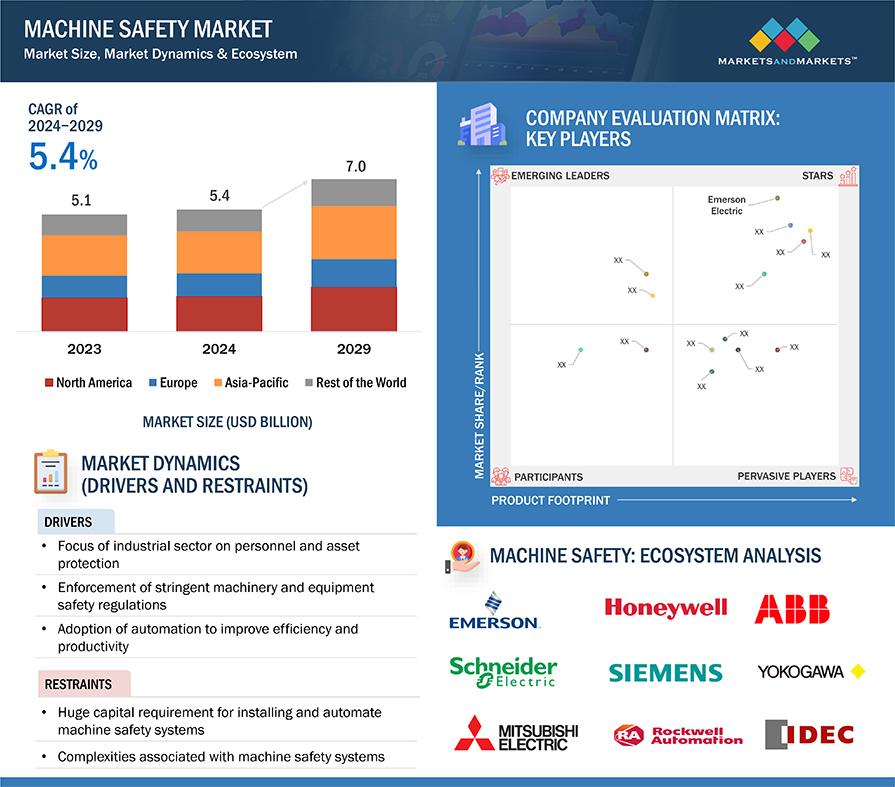
The machine safety market will grow from USD 5.4 billion in 2024 to USD 7.0 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 5.4% during the same period.
The major players in the market are Schneider Electric (France), Honeywell International, Inc. (US), ABB (Switzerland), Rockwell Automation, Inc. (US), Siemens AG (Germany), OMRON Corporation (Japan), Keyence Corporation (Japan), Yokogawa Electric Corporation (Japan), Emerson Electric Co. (US), General Electric (US), Mitsubishi Electric Corporation (Japan), Sick AG (Germany), HIMA (Germany), and IDEC Corporation (Japan).
Download PDF Copy:
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=1188
Driver: Adoption of automation to improve efficiency and productivity
Recently, industrial automation has risen significantly to bring about cost savings and quality control. Industrial automation, such as robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, would also help companies increase plant efficiency and productivity by automating repetitive tasks and reducing errors. Such automated systems will keep working quickly and accurately, reducing production time and cost while increasing output. However, industrial automation also brings another risk: machines and equipment can be hazardous if not correctly designed, installed, and maintained. The amount and complexity of machinery and equipment used in manufacturing, production, and other industries will increase progressively, thus growing danger to people's lives through industrial automation.
Restraint: Complexities associated with machine safety systems
One of the major factors hindering the growth of the machine safety market is the lack of awareness about the advantages of using these systems. Emerging economies are still unaware of the availability of safety devices that can safeguard machinery and labor. Most manufacturers do not appoint safety experts who advise adopting the safety devices necessary for each machine or process. Secondly, even if end users know the benefits of safety devices, development and integration-related complexities restrict their implementation. Certified and trained mechanical, electronics, and software engineers and industrial safety management professionals must work cohesively to design robust safety management devices. The challenge is increased further while installing and validating the system. Ensuring that the entire system meets the requirements of SIL is very essential. Another important factor is setting systems at correct performance standards to realize the possible economic benefits.
Opportunity: Increasing awareness about workplace safety standards in emerging economies
Workplace safety standards developed locally and internationally by regulatory and standard-making bodies have found their way into the workplace environment in developed countries, such as the US, the UK, France, Australia, Japan, and the Netherlands. The governments of these countries have enforced laws against industries that are not maintaining the set rules, which are meant to protect human and equipment assets. However, emerging economies are still way behind in adapting to machine safety systems. It is essential to mention that the manufacturing industry in certain countries, for example, South Korea, India, and China, has flourished in the last decade with inexpensive and readily available human resources. At the same time, these countries have very little concern for occupational safety and have recently adopted a move to argue and protest from worker unions to maintain safety standards in the industries.
Challenge: Failure to assess and anticipate all potential risks associated with machinery setup
A comprehensive machine guarding requires the risk assessment input of all parties, including guard designers, machine operators, maintenance, supervisors, engineers, safety professionals, and machine guarding experts, not excluding the OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer). A designer has a task that may be overwhelming in anticipating all possible hazards when setting up equipment, operation, inspection, or maintenance. Careful planning and implementation are necessary if workers need to enter areas inside the machine guards. Even then, the upfront work of performing a risk assessment can overlook some very critical specifications for the design and performance criteria of safety-related components—including interlock devices and monitoring components like relays, as well as safety-rated programmable logic controllers that enforce protection when using the alternative safeguarding methods.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Startseite
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Andere
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


