"Celestial Connections: The Rise of Satellite Communication"
Introduction
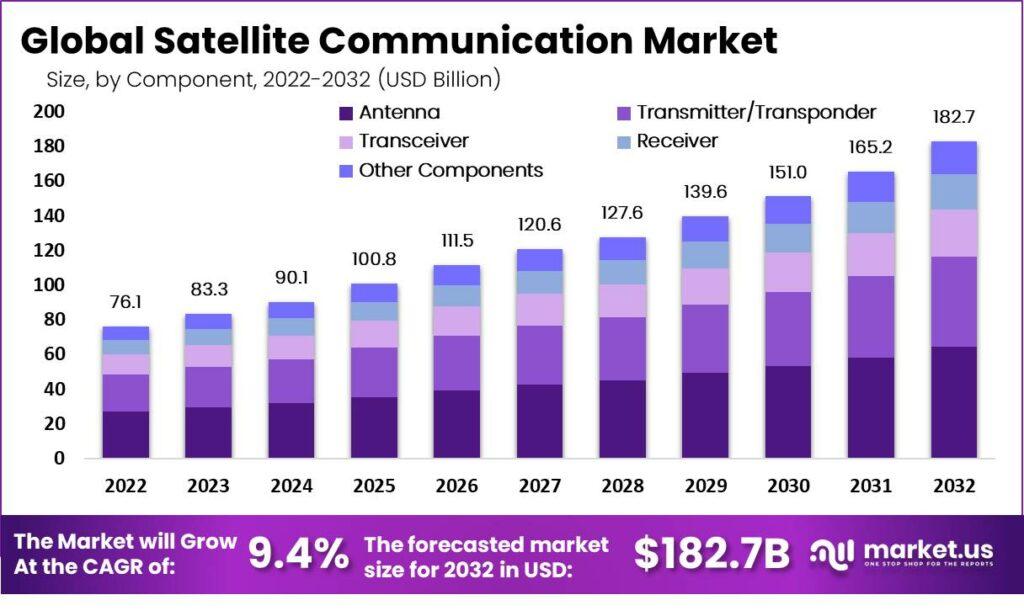
The Satellite Communication (Satcom) market has seen significant growth due to the increasing demand for global connectivity, the expansion of broadband services, and advancements in satellite technology. As more industries rely on seamless communication, especially in remote and rural areas, satellites offer a critical solution.
Read More - https://market.us/report/satellite-communication-market/
Moreover, the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, 5G technology, and high-definition broadcasting has further fueled this demand. However, the market faces challenges such as the high costs of satellite deployment and maintenance, regulatory hurdles, and the complexities of integrating satellite systems with terrestrial networks. For new entrants, there are exciting opportunities, particularly in developing innovative satellite-based services, low-cost satellite manufacturing, and leveraging emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enhance satellite operations.
Emerging Trends
-
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites: These satellites, positioned closer to the Earth, are becoming more popular due to their ability to provide low-latency, high-speed internet services, especially in underserved regions.
-
Satellite IoT: As the number of IoT devices grows, the use of satellites to connect these devices globally is emerging as a key trend. This is particularly important for industries like agriculture, logistics, and environmental monitoring.
-
5G Integration: The integration of satellite communication with 5G networks is gaining traction, as it helps extend the reach of 5G services to remote and rural areas, ensuring broader coverage.
-
Advanced Ground Systems: Innovations in ground station technology, such as electronically steerable antennas, are improving the efficiency and reliability of satellite communications.
-
Sustainability Initiatives: With growing concerns about space debris, there’s a trend toward developing sustainable satellite systems, including those that can be de-orbited at the end of their lifecycle to minimize space pollution.
Top Use Cases
-
Global Broadband Coverage: Satellite communication is critical for providing high-speed internet to remote and rural areas where traditional terrestrial infrastructure is lacking.
-
Disaster Management: In times of natural disasters, satellites provide essential communication services when ground-based networks are damaged or overloaded.
-
Maritime and Aviation: Satcom is vital for communication in the aviation and maritime industries, ensuring connectivity in areas far from terrestrial networks.
-
Military and Defense: Satellites are extensively used for secure communication, surveillance, and reconnaissance by military forces worldwide.
-
Broadcasting: Satellites play a key role in broadcasting television and radio signals globally, ensuring that content reaches even the most isolated areas.
Major Challenges
-
High Costs: The cost of developing, launching, and maintaining satellites is extremely high, posing a significant barrier for many companies.
-
Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the complex web of international regulations and securing the necessary licenses for satellite operations can be challenging.
-
Space Debris: The increasing amount of space debris poses a risk to satellites, potentially leading to collisions and operational failures.
-
Technological Integration: Integrating satellite systems with existing terrestrial networks and emerging technologies like 5G can be complex and expensive.
-
Cybersecurity Risks: As satellites become more interconnected, they are increasingly vulnerable to cyber-attacks, which can compromise their operations.
Market Opportunities
-
Rural Connectivity: There is a significant opportunity for companies to provide broadband services to underserved rural and remote areas, bridging the digital divide.
-
IoT Expansion: With the rise of IoT, there’s potential for satellite communication providers to offer global connectivity solutions for a wide range of IoT applications.
-
Space Tourism and Exploration: As the space tourism industry grows, satellite communication will be crucial for ensuring reliable communication and navigation.
-
AI and Automation: Leveraging AI and automation in satellite operations can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance service reliability.
-
New Market Entrants: Startups focused on developing small, cost-effective satellites or providing niche satellite services can carve out a place in the market.
Conclusion
The Satellite Communication market is on an upward trajectory, driven by the increasing demand for global connectivity and advancements in satellite technology. While the market presents some challenges, such as high costs and regulatory complexities, the opportunities it offers—especially in rural connectivity, IoT, and new technological integrations—are immense.
Emerging trends like LEO satellites, satellite IoT, and 5G integration highlight the dynamic nature of the market, paving the way for innovative solutions and new players. As the industry continues to evolve, those who can navigate the challenges and seize the opportunities will find themselves at the forefront of a market that is essential for the future of global communication.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


