How Advanced Neurosurgical Simulators Are Enhancing Surgeon Skill and Confidence?
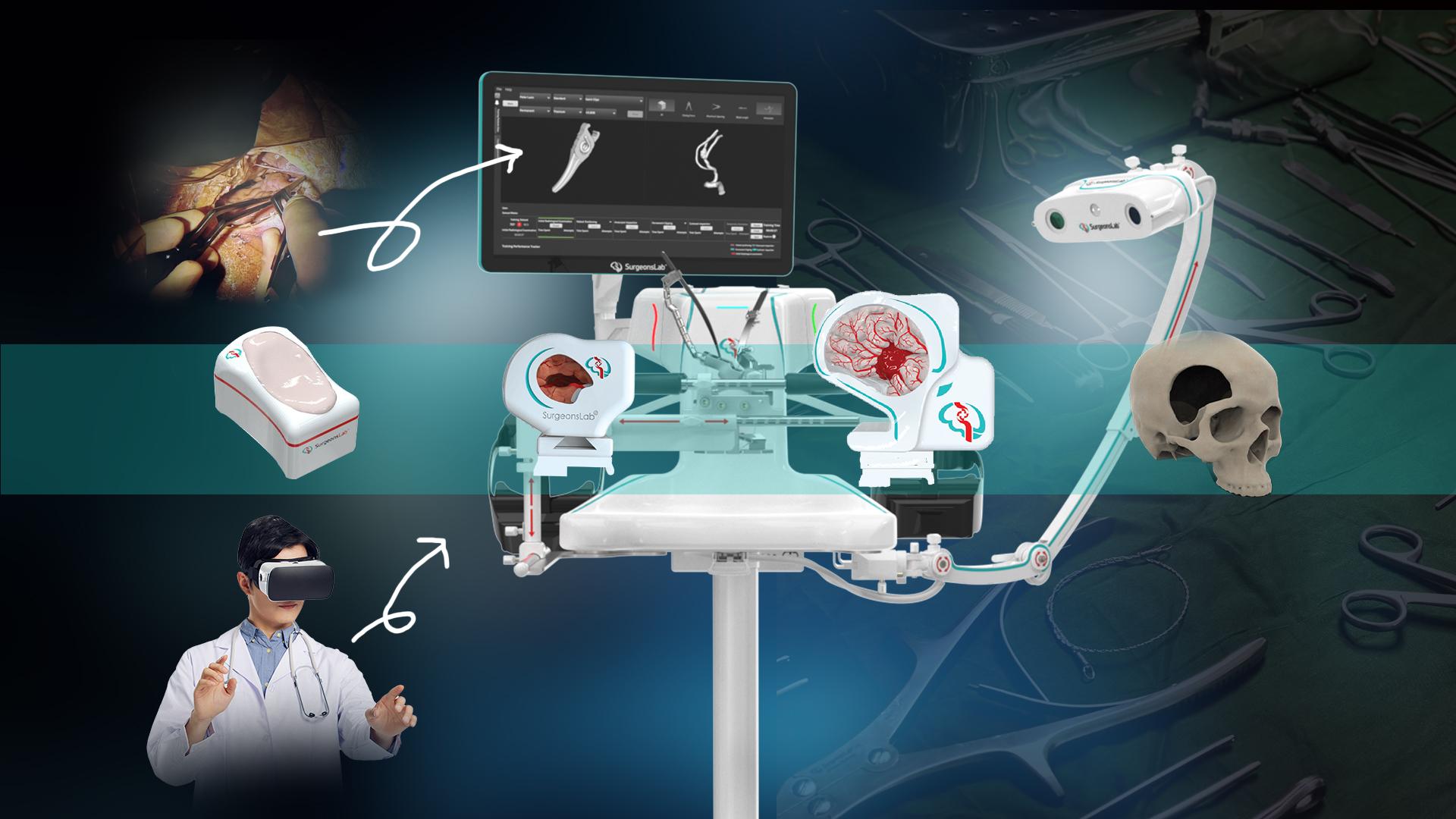
Neurosurgery practice, which deals with very fine procedures requiring utmost precision, has seen simulators revolutionize the preparation process of surgeons while handling intricate procedures. This article discusses the contribution of neurosurgical simulator software, especially in relation to CT simulation and radiation therapy, to the upgrading of surgeon dexterity and confidence.
The Power of Simulation in Neurosurgery
Neurosurgical simulators provide a virtual environment that accurately reflects the details of a human brain, which is approximately a completely risk-free environment where surgeons can practice and hone their techniques. SurgeonsLab has one very interesting software for surgical training that has won fame for realistic simulations. The digital version of the operating room permits neurosurgeons to navigate through the various neurosurgical scenarios- from simple resections of brain tumors to intricate vascular procedures-all that could be experienced in real-life conditions within the simulated room.
It mainly features CT (Computerized Tomography) simulation. Institutions like NewYork-Presbyterian have the CT Simulator, which provides a very detailed 3D image of a patient's inside anatomy. These images have thus become the basis of highly accurate simulations. This way, surgeons get to view and interact with the actual anatomical structures they would operate on in the actual process.
Enhancing Surgeon Skill and Confidence
-
Realistic Training: Simulators in neurosurgery provide the most immersive experience for surgeons, allowing them to repeat procedures in a safe environment. Repeated practice fosters muscle memory, enhances hand-eye coordination, and also gives a general impression of a more skillful surgeon.
-
Customized Learning: Simulators can be designed for specific trainee surgeons; the simulator may focus on certain kinds of procedures that often occur or even rare cases. This specificity is very effective in speeding up the learning process and bringing confidence.
-
Error Analysis: High fidelity simulators give immediate feedback, which focuses on where improvement is needed. Surgeons would be able to redo the performance, identify their mistakes, and adjust those mistakes appropriately, thus coming up with a more advanced surgical practice.
-
Preoperative Radiosurgery Planning: CT simulation is gold in radiation oncology. It would help provide close to precise placement of areas of interest as well as the planning site; thus, radiation therapy can be delivered accurately and as safely as possible.
Key Takeaway
In conclusion, neurosurgical simulators combined with CT simulation radiation therapy technology improve surgical performance and confidence. Such simulator versions offer a very realistic and controlled training atmosphere by which neurosurgical education is being reshaped, and positive patient outcomes are achieved.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


