3D-IC: Revolutionizing Semiconductor Technology
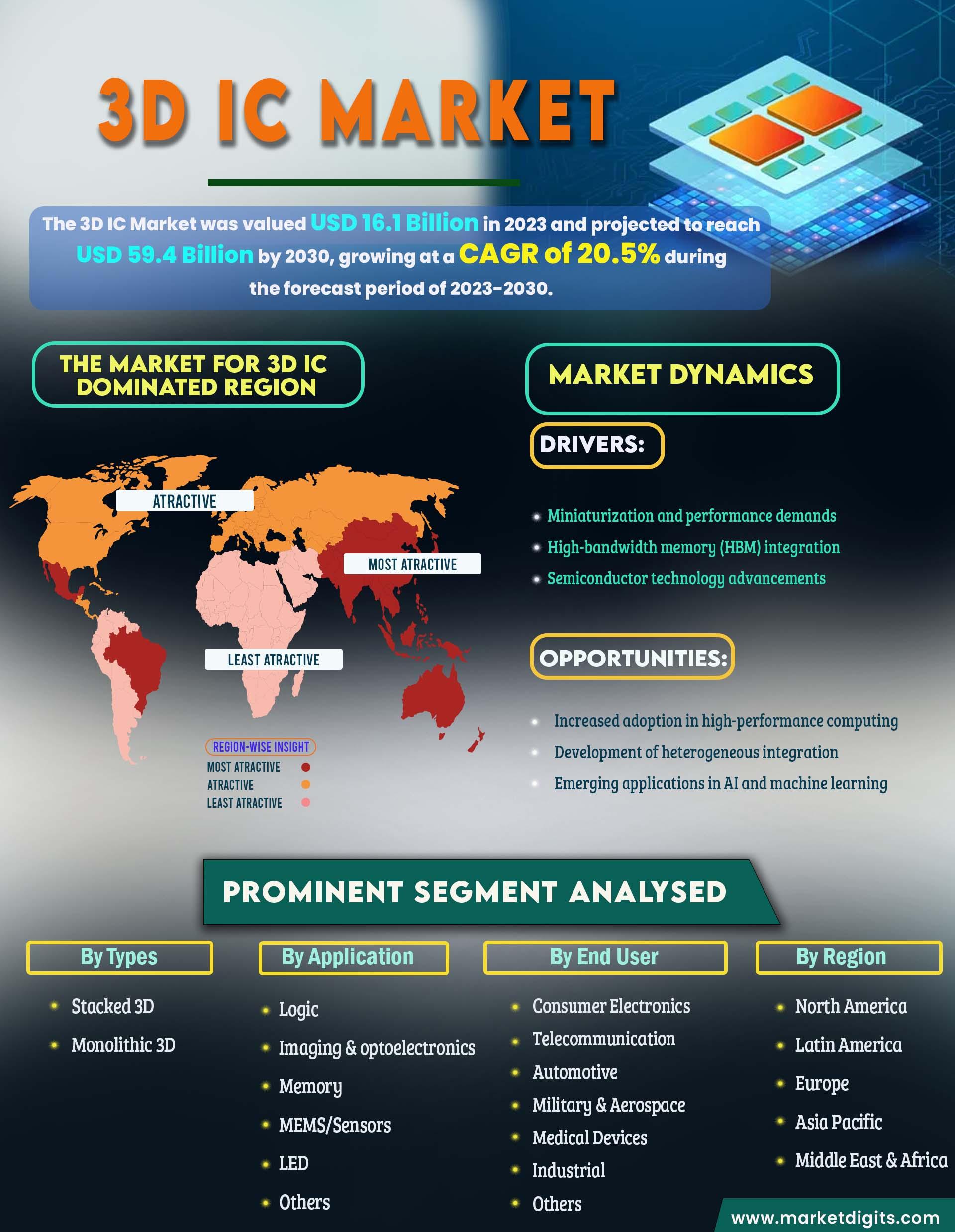 3D Integrated Circuits (3D-IC) represent a significant advancement in semiconductor technology, aiming to enhance the performance and efficiency of microelectronic devices. Unlike traditional 2D ICs, which are laid out on a single plane, 3D-ICs involve stacking multiple layers of electronic components vertically.This vertical integration allows for shorter interconnects between layers, leading to faster data transfer and reduced power consumption.The primary advantage of 3D-ICs is their ability to pack more functionality into a smaller footprint. As the demand for miniaturization in electronics continues to grow, 3D-ICs offer a viable solution by enabling higher density and better performance without expanding the chip size. This is particularly beneficial in applications like smartphones, wearable devices, and high-performance computing, where space is at a premium.
3D Integrated Circuits (3D-IC) represent a significant advancement in semiconductor technology, aiming to enhance the performance and efficiency of microelectronic devices. Unlike traditional 2D ICs, which are laid out on a single plane, 3D-ICs involve stacking multiple layers of electronic components vertically.This vertical integration allows for shorter interconnects between layers, leading to faster data transfer and reduced power consumption.The primary advantage of 3D-ICs is their ability to pack more functionality into a smaller footprint. As the demand for miniaturization in electronics continues to grow, 3D-ICs offer a viable solution by enabling higher density and better performance without expanding the chip size. This is particularly beneficial in applications like smartphones, wearable devices, and high-performance computing, where space is at a premium.
Moreover, 3D-ICs facilitate heterogeneous integration,allowing different types of materials and technologies to be combined on a single chip.This enables the integration of memory, logic, and sensor components, enhancing the overall capabilities of the device.Despite their advantages, 3D-ICs face challenges such as thermal management and manufacturing complexity. However, ongoing research and advancements in fabrication techniques are addressing these issues, making 3D-ICs a promising technology for the future of electronics.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Giochi
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Altre informazioni
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


