Mango Price Trend: An In-Depth Analysis
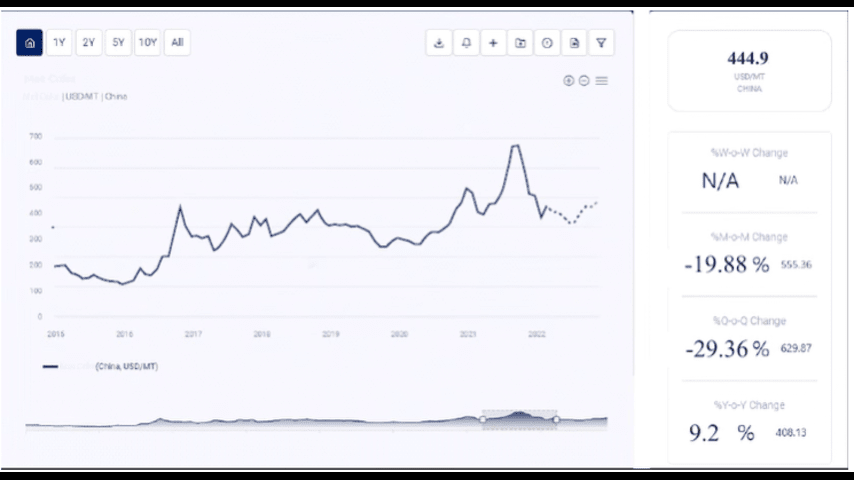
Mangoes, often referred to as the "King of Fruits," are not only one of the most beloved tropical fruits globally but also play a crucial role in the agricultural economies of many countries. Known for their rich taste, vibrant colour, and nutritional value, mangoes are grown in over 100 countries, with India being the largest producer, followed by China, Thailand, and Indonesia.
The price of mangoes is subject to several factors, from weather conditions and seasonal fluctuations to transportation costs and international trade dynamics. As a result, the mango price graph can fluctuate significantly, depending on the production levels, global demand, and other market forces. In this article, we will explore the factors that influence mango prices, review historical price trends, and discuss future expectations for the mango market.
1. Key Factors Affecting Mango Prices
The price of mangoes can fluctuate due to various factors, including climatic conditions, supply chain issues, and market demand. Understanding these factors is essential for producers, retailers, and consumers to anticipate price trends and make informed decisions.
1.1 Weather Conditions and Climate Impact
Mangoes are highly sensitive to weather conditions, and their yield can be significantly impacted by climatic changes. Adverse weather events such as droughts, floods, and storms can reduce mango production, causing a shortage in supply and driving prices higher. Additionally, unusual temperature patterns can affect fruit quality and harvesting times, further impacting the availability and cost of mangoes.
-
Seasonal Variability: Mangoes have a specific growing season that varies by region. In tropical and subtropical areas, the season typically peaks during summer. However, unexpected shifts in the weather or climatic patterns, such as the El Niño phenomenon, can affect the flowering and fruit-bearing process, causing disruptions in supply and influencing prices.
-
India’s Monsoon: In countries like India, which accounts for more than 40% of global mango production, the monsoon season plays a significant role in determining the crop yield. A delay or failure of the monsoon can lead to a lower yield, consequently pushing up prices.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/mango-price-trends/pricerequest
1.2 Supply Chain and Transportation Costs
Mangoes are highly perishable fruits, and their journey from farm to market requires careful handling and timely transportation. Therefore, supply chain inefficiencies, including delays, labor strikes, or high fuel costs, can significantly impact mango prices. When transportation costs increase, particularly due to rising fuel prices or logistical challenges (such as border controls, trade restrictions, or truck driver shortages), the cost of getting mangoes to market also rises.
-
Export-Import Dynamics: Mangoes are traded internationally, with major exporters including India, Mexico, and Thailand, while major importers are the United States, the European Union, and the Middle East. Any trade disruptions, tariffs, or logistical bottlenecks can affect mango prices in both the exporting and importing countries.
-
Cold Storage: Since mangoes have a short shelf life, cold storage facilities play a crucial role in maintaining their quality during transport. The cost of maintaining cold storage infrastructure, along with energy prices, can affect the overall price of mangoes.
1.3 Demand and Consumer Preferences
The global demand for mangoes has grown significantly over the years, driven by the increasing popularity of tropical fruits and the rise of healthy eating trends. The demand for mangoes tends to peak during their harvest season, but variations in consumer preferences, changing tastes, and cultural influences can also affect prices.
-
Global Consumption: The demand for mangoes is growing in developed markets like the United States and Europe, where consumers are becoming more health-conscious and seeking nutritious, exotic fruits. The rise in the popularity of mango-based products such as juices, smoothies, ice cream, and dried mangoes further contributes to increased demand and higher prices.
-
Festivals and Cultural Events: Mangoes are an integral part of many cultural and religious celebrations, especially in countries like India, where they are often featured during festivals such as Diwali and Makar Sankranti. During such times, demand spikes, which can lead to price increases.
1.4 Agricultural Practices and Productivity
Advancements in agricultural practices and improvements in crop management can help stabilize mango prices by increasing yield and improving fruit quality. The use of better irrigation techniques, disease-resistant varieties, and sustainable farming practices can enhance productivity, reduce losses, and ensure a steady supply of mangoes.
-
Farm Size and Scale: Larger, more efficient farms can often produce mangoes at a lower cost due to economies of scale. Conversely, small-scale farmers may struggle with higher production costs, leading to higher prices.
-
Pest Control and Fertilization: Mango farming is vulnerable to various pests and diseases, which can lead to crop loss or reduced fruit quality. Farmers must invest in pest control measures and high-quality fertilizers, which can increase the cost of production and, consequently, the price of mangoes.
1.5 International Trade Policies
Trade policies and tariffs also play a significant role in mango price trends. Governments in mango-producing countries may introduce subsidies or support measures to boost local production, while trade agreements between countries can affect the import/export of mangoes and influence their prices.
-
Tariffs and Trade Restrictions: Any trade restrictions, tariffs, or quotas imposed on mango exports can result in higher prices in importing countries. For example, if a major mango-exporting country faces a trade dispute with a significant importer, it can reduce supply, leading to price increases in the importing country.
-
Market Access: In some cases, mangoes from certain regions may be banned or restricted due to concerns over pests or diseases. These restrictions can disrupt supply chains and lead to price fluctuations.
2. Historical Mango Price Trends
2.1 Price Stability in Early 2010s
Throughout the early 2010s, mango prices were relatively stable, with moderate fluctuations due to typical seasonal variations and minor disruptions in supply. During this period, global mango production was steady, and the primary factors influencing prices were regional harvests and seasonal changes. For example, in countries like India and Mexico, the harvests were largely in line with expectations, leading to a steady supply in global markets.
- Stable Export Prices: Major exporters like India and Mexico maintained consistent export levels, while demand remained stable from key importing countries such as the United States and the European Union.
2.2 Price Surge in 2016-2018
Between 2016 and 2018, mango prices saw a significant rise due to adverse weather conditions and poor harvests in key producing countries. Unfavorable weather patterns, including storms and droughts, impacted yields in tropical regions, particularly in India and Thailand, two of the largest producers of mangoes.
- Weather Disruptions: The 2016 Indian monsoon, for instance, was particularly delayed and weaker than usual, leading to a reduced mango harvest. This caused a price spike both in domestic and international markets, as global demand outstripped the available supply.
2.3 Volatility and Price Fluctuations in 2020-2022
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the global mango market, causing both disruptions in supply chains and fluctuations in demand. Initially, prices dropped as demand for fresh fruit fell during lockdowns. However, as supply chains were disrupted and international trade slowed down, prices began to rise due to lower supply.
-
Pandemic Impact: With disruptions to transportation and cold storage facilities, the cost of bringing mangoes to international markets increased. At the same time, the demand from home consumers and online grocery shopping surged, creating a shift in consumption patterns that affected prices.
-
Supply Chain Recovery: As the global economy started recovering from the pandemic in 2021, demand for mangoes rebounded, particularly in Europe and North America, further influencing price increases.
2.4 Current Price Trends in 2023 and Beyond
As of 2023, mango prices have stabilized to some extent following the volatility caused by the pandemic. However, challenges such as inflation, high fuel prices, and adverse weather events continue to impact the cost structure of mango production and distribution. The prices of mangoes in the international market remain on an upward trajectory due to growing demand, especially from emerging economies and health-conscious consumers in developed countries.
-
High Demand in Emerging Markets: In countries like China, the Middle East, and Africa, rising disposable incomes and changing diets have led to an increase in mango consumption, putting upward pressure on prices.
-
Agricultural Adjustments: On the production side, improvements in farming practices, such as the adoption of more resilient mango varieties, are helping to mitigate some price increases, but challenges like climate change and water shortages are still significant concerns.
3. Future Outlook for Mango Prices
3.1 Increased Demand for Bio-Based Products
With growing demand for mango-based products such as mango puree, juices, and dried mangoes, the future demand for mangoes will likely increase, especially in emerging markets. This could put additional pressure on prices, particularly if production challenges persist.
- Mango-Related Products: As the demand for healthy and natural ingredients in food products increases, more manufacturers may look to mangoes as a key ingredient in smoothies, desserts, and packaged foods, further driving up prices.
3.2 Sustainability and Environmental Challenges
The long-term price trends of mangoes will be influenced by how well producers adapt to climate change and environmental challenges. Those that invest in sustainable farming practices and more water-efficient methods will likely face less volatility in pricing. However, those who rely on outdated farming techniques or face frequent weather disruptions may experience higher production costs, impacting prices.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Numbers:
- USA & Canada: +1 307 363 1045
- UK: +44 7537171117
- Asia-Pacific (APAC): +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


