Solid Waste Management Market Manufacturers, Types, Regions and Application Research Report, 2032
Solid waste management is a critical component of urban infrastructure, aimed at minimizing the environmental and health impacts of waste generated by households, industries, and institutions. It encompasses the systematic collection, transportation, processing, recycling, and disposal of waste materials in compliance with environmental regulations. With urbanization and population growth escalating worldwide, cities are facing increasing challenges in managing solid waste efficiently. Modern solid waste management systems integrate advanced technologies such as waste-to-energy conversion, material recovery facilities, and smart waste management solutions to improve sustainability. These systems not only mitigate environmental hazards but also promote resource conservation and circular economy practices.
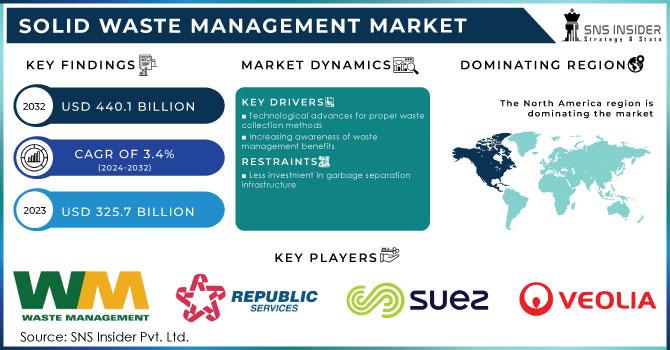
The Solid Waste Management Market Size was valued at USD 325.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 440.1 billion by 2032, and grow at a CAGR of 3.4% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Future Scope
The future of solid waste management lies in the adoption of innovative and sustainable practices to address the challenges posed by rising waste volumes. The global shift toward a circular economy is expected to drive investments in recycling and material recovery technologies, ensuring that waste is treated as a resource rather than a liability. Emerging economies are anticipated to play a pivotal role in the market as they enhance their waste management infrastructure to meet growing urban demands. Waste-to-energy technologies, such as anaerobic digestion and advanced incineration systems, are set to gain prominence, providing renewable energy while reducing landfill dependency. Additionally, digitalization in waste management, including IoT-enabled monitoring and AI-driven optimization, will transform the sector, enabling more efficient and transparent operations.
Emerging Trends
The solid waste management industry is witnessing several transformative trends. Smart waste management systems, which use IoT sensors and data analytics to optimize waste collection and processing, are becoming increasingly popular in urban areas. Waste segregation at source is gaining traction, facilitated by public awareness campaigns and government incentives. Recycling technologies are advancing, with chemical recycling methods allowing the breakdown of complex plastics into reusable raw materials. Additionally, the concept of zero waste cities is emerging, with municipalities implementing policies to divert the majority of their waste away from landfills. Waste-to-energy projects, such as biogas plants and incinerators with energy recovery capabilities, are also expanding globally, contributing to both energy security and waste reduction.
Drivers
The growing urban population and rapid industrialization are primary drivers of the solid waste management market. Governments worldwide are introducing stringent regulations to curb the environmental impacts of improper waste disposal, thereby fostering the adoption of advanced waste management solutions. Public awareness of environmental issues, including the harmful effects of plastic pollution and greenhouse gas emissions from landfills, is pushing both individuals and corporations toward sustainable waste management practices. The increasing focus on renewable energy sources, coupled with the need to reduce landfill usage, is driving the growth of waste-to-energy initiatives. Furthermore, advancements in technology and rising investments in smart city projects are encouraging the implementation of intelligent waste management systems.
Restraints
Despite its critical importance, the solid waste management sector faces several challenges. High initial investment costs for infrastructure development, such as waste-to-energy plants and advanced recycling facilities, can deter implementation, particularly in developing regions. Inefficient waste segregation and collection practices hinder the effectiveness of recycling and resource recovery. Additionally, a lack of public awareness and participation in waste reduction and segregation efforts remains a significant barrier. Regulatory inconsistencies and inadequate funding for waste management programs in some regions further complicate the adoption of sustainable practices. The environmental and social opposition to the establishment of landfills and incineration facilities also poses challenges to the industry.
Key Points
· Solid waste management involves the systematic handling of waste through collection, transportation, processing, recycling, and disposal.
· It plays a vital role in reducing environmental pollution, conserving resources, and supporting sustainable urban development.
· The market is driven by urbanization, environmental regulations, public awareness, and advancements in waste-to-energy and recycling technologies.
· Emerging trends include smart waste management systems, chemical recycling, and zero waste city initiatives.
· Challenges include high infrastructure costs, inefficient waste segregation, lack of public awareness, and regulatory inconsistencies.
Solid waste management is at the forefront of global efforts to combat environmental degradation and promote sustainability. By embracing innovative technologies and fostering public-private partnerships, the sector is poised to revolutionize waste handling and resource recovery, paving the way for a cleaner, greener future.
Get Free Sample Copy @ https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/3411
Contact Us:
Akash Anand – Head of Business Development & Strategy
Phone: +1-415-230-0044 (US) | +91-7798602273 (IND)
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jocuri
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Alte
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


