Peripheral Vascular Devices: Revolutionizing Interventional Cardiology
Peripheral Vascular Devices have ushered in a new era of interventional cardiology, revolutionizing the approach to managing and treating a wide range of vascular conditions. Historically, cardiovascular diseases were associated with high morbidity and mortality rates. However, with the advent of these groundbreaking devices, medical professionals can now provide less invasive and more effective treatments, greatly improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
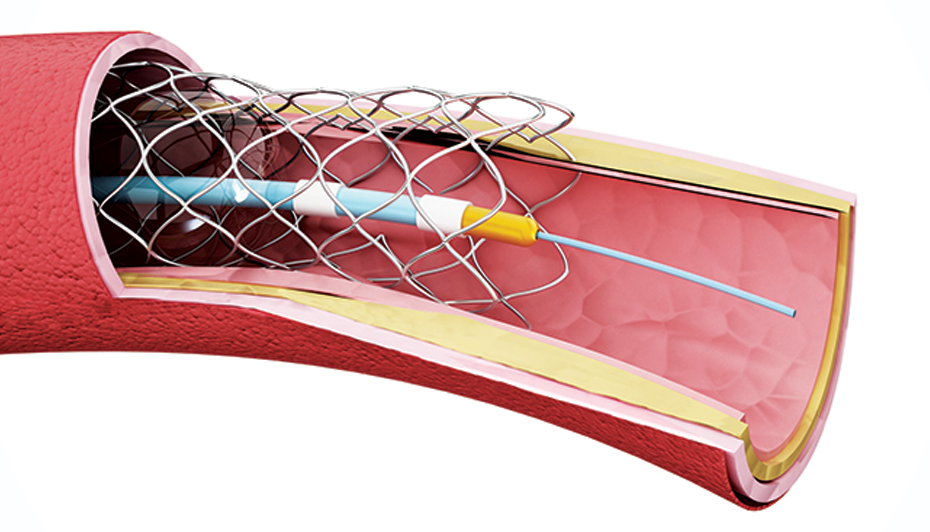
One of the key innovations that has transformed interventional cardiology is the development of catheter-based therapies. These procedures, collectively known as endovascular interventions, involve accessing the vascular system through small incisions and guiding specialized catheters to the affected areas. Balloon angioplasty and stent implantation are prime examples of such treatments. These minimally invasive approaches have reduced the need for open surgeries, leading to shorter hospital stays, faster recoveries, and lower complication rates.
Drug-eluting stents (DES) have also played a critical role in revolutionizing peripheral vascular interventions. These stents are coated with medications that inhibit tissue growth, reducing the risk of restenosis or re-narrowing of treated arteries. The integration of DES technology has significantly increased the long-term success of stent placements, making it a preferred choice for complex vascular lesions and challenging patient cases.
Market research conducted by Coherent Market Insights indicates a promising outlook for the Global Peripheral Vascular Devices Market. Expected to reach a significant value of US$ 10,266.8 million by 2022, the market is poised for growth with an anticipated CAGR of 7.6% during the forecast period spanning from 2022 to 2030. The increasing prevalence of peripheral vascular diseases, including Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD), is identified as a major factor driving market expansion. Notably, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported that as of September 27, 2021, a staggering 6.5 million individuals aged 40 and older in the U.S. have been diagnosed with PAD.Top of Form
Another exciting advancement is the use of advanced imaging techniques during interventions. Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) provide real-time, high-resolution images of blood vessels, allowing physicians to assess vessel morphology, plaque burden, and stent apposition with exceptional precision. The integration of such imaging modalities has improved procedural planning and enhanced the overall safety and effectiveness of peripheral vascular interventions.
Moreover, the development of embolic protection devices has proven instrumental in safeguarding against potentially harmful debris during certain procedures. These devices capture and remove emboli (tiny particles) that may break off from the arterial walls, reducing the risk of complications, such as strokes or other organ damage.
Additionally, researchers are exploring the use of bioresorbable scaffolds, which are stents that gradually dissolve over time, leaving behind a restored natural vessel. This approach eliminates the potential long-term issues associated with permanent stent placement and offers a more patient-friendly alternative for specific cases.
In conclusion, Peripheral Vascular Devices have revolutionized the field of interventional cardiology, enabling physicians to provide state-of-the-art, minimally invasive treatments for patients with vascular diseases. As technology continues to advance, these devices will play an increasingly critical role in shaping the future of cardiovascular care, leading to improved patient outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and a healthier global population.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


