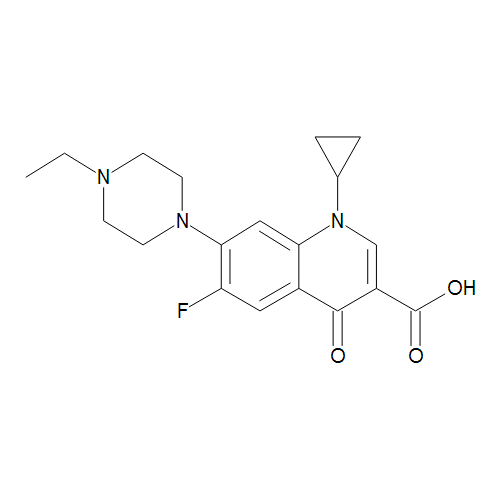
Chemical Properties and Mechanism of Action
Enrofloxacin contains a bicyclic fluoroquinolone core structure which is responsible for its bactericidal properties. It works by inhibiting the bacterial enzymes DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV which are required for DNA replication, transcription, repair and recombination. This leads to bacterial cell death. Chemically, enrofloxacin is a white to slightly yellowish crystalline powder. It is very soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol and chloroform. Its molecular formula is C19H22FN3O3 and molecular weight is 360.4 g/mol.
Spectrum of Antibacterial Activity
Enrofloxacin has broad spectrum antibacterial activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It is highly effective against respiratory and enteric pathogens like Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., Mycoplasma spp., Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus. It is also active against intracellular pathogens like Chlamydia psittaci. This broad spectrum of activity makes enrofloxacin useful for treating mixed infections in animals.
Get More Insights on Enrofloxacin