From Diagnosis to Recovery: Improving Quality of Life with Gout Disease Treatment
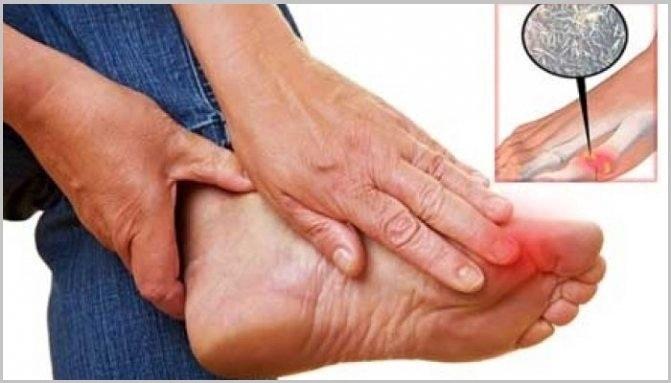
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden, severe attacks of pain, swelling and tenderness in joints, usually the joint at the base of the big toe. It occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, tissues or kidneys. Uric acid is a waste product produced during the breakdown of purines — chemical compounds that are part of many foods we eat. Gout occurs when uric acid builds up and forms needle-like urate crystals in the lining of joints and surrounding tissues.
Causes and Risk Factors of Gout
The exact cause of Gout Disease Treatment is unknown, but certain risk factors are known to increase the likelihood of developing gout, including diet, family history, other medical conditions and medications. Consuming foods high in purines like meat, seafood and alcohol can raise uric acid levels in the blood. Genetic factors play a role too, as people with certain genes involved in uric acid transport are predisposed to developing gout. Other conditions like obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure and medications used to treat these diseases may also raise the risk. Men are more likely to develop gout than women before menopause, when levels of estrogen - a natural diuretic - are higher in females.
Symptoms of Gout
The most common symptom is a red, tender, hot, swollen joint, usually the joint at the base of the big toe. Other joints may also be affected like the ankle, knees, feet or fingers. The onset of symptoms is often sudden, occurring at night, and peaks within 12 to 24 hours. Excruciating pain during an attack of gout may make it difficult to walk or stand. As the flare subsides, small, hard lumps under the skin or tissue (tophi) may form around the affected joint. Tophi are deposits of urate crystals and can cause joint damage if untreated long-term.
Get More Insights On- Gout Disease Treatment
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Juegos
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


