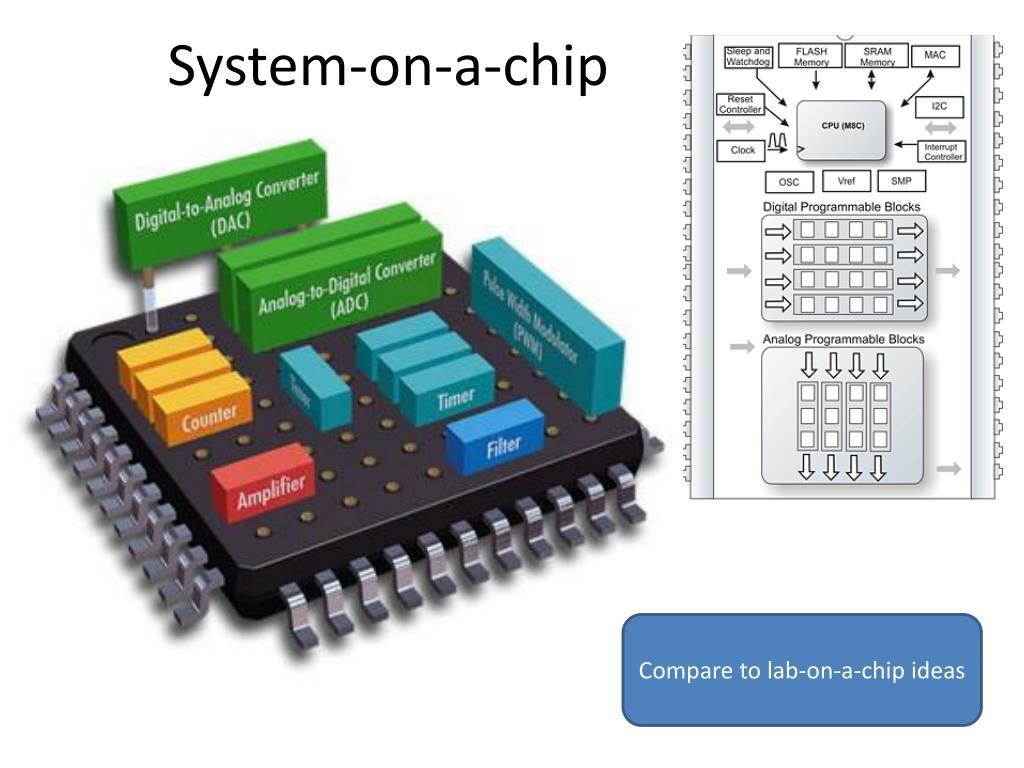
What is it?
A System on a Chip, also known as SoC, refers to integrating all the components of a computer or other electronic system into a single integrated circuit (IC) chip. Some key components that are typically integrated into a SoC include a central processing unit (CPU), memory, input/output ports, and other digital components typically found in a complete computer system. By integrating all these components onto a single chip, SoCs help reduce costs, improve performance, and lower power consumption compared to using multiple discrete components.
A Brief History of System on a Chip Development
The concept of an system on a chip can be traced back to the late 1980s when basic microcontrollers started combining CPU and memory on a single chip. In the 1990s, advances in CMOS technology allowed for even higher levels of integration, with basic SoCs emerging that combined CPU, memory and peripherals. By the early 2000s, advanced CMOS processes enabled full-fledged systems-on-chip that incorporated complex CPUs, graphics processors, large memory subsystems and various interfaces all on a single die. Today's smartphones, tablets and other mobile devices extensively utilize ultra high-density SoCs containing billions of transistors enabling very powerful systems to fit inside small, portable form factors.
Processor Technology Advances
A key factor driving SoC evolution has been continual advancement in processor technology. Early SoC CPUs were 8-bit or 16-bit cores with limited functionality. However, with each new processor generation, manufacturers were able to significantly increase performance while reducing power and die size. Modern SoC processors employed in smartphones and IoT devices now feature high-performance 64-bit architectures, multiple and heterogeneous cores, and specialized compute units for graphics, AI and other tasks. Advanced processors allow SoCs to comfortably run complex operating systems and applications.
Get more insights on This Topic- System On A Chip