Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Autoimmune Disease Diagnosis
The field of autoimmune disease diagnosis has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, driven by increasing prevalence and awareness of autoimmune disorders such as Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), Thyroiditis, and Scleroderma. These conditions, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, affect millions worldwide and pose challenges in accurate and timely diagnosis. The global autoimmune disease diagnosis market, segmented by these prevalent conditions, reflects the growing demand for effective diagnostic tools and technologies.
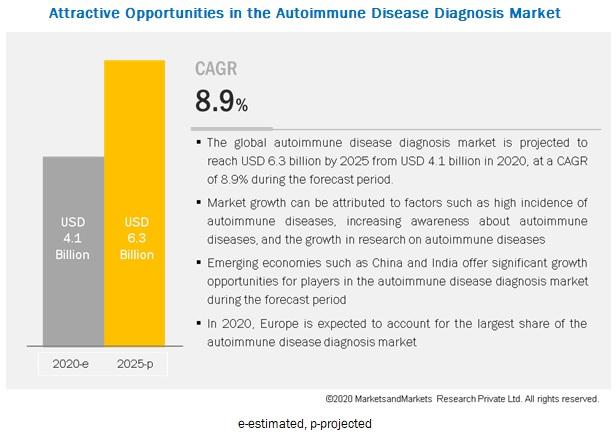
Autoimmune Disease Diagnosis Market Size by Disease (RA, SLE, Thyroiditis, Scleroderma) – Global Forecast to 2025
Autoimmune disease diagnosis market in terms of revenue was estimated to be worth $4.1 billion in 2020 and is poised to reach $6.3 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 8.9%
Download a PDF Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=174826519
Understanding Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases are a diverse group of disorders characterized by an abnormal immune response against the body's own cells and tissues. This results in inflammation, tissue damage, and sometimes organ dysfunction. RA, an inflammatory arthritis affecting joints, is one of the most common autoimmune diseases, affecting over 1.3 million people in the United States alone. SLE, commonly known as lupus, can affect various organs and systems, leading to a range of symptoms from joint pain to kidney damage. Thyroiditis involves inflammation of the thyroid gland, impacting hormone production and metabolism, while Scleroderma causes hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues.
Market Dynamics
The autoimmune disease diagnosis market is influenced by several factors, including increasing disease prevalence, advancements in diagnostic technologies, and growing healthcare expenditure globally. According to recent studies, autoimmune diseases collectively affect about 5-8% of the population in developed countries, with varying prevalence rates among different conditions. This prevalence drives the demand for accurate and early diagnosis, enabling timely intervention and management of these chronic conditions.
Diagnostic Technologies and Innovations
Diagnostic modalities for autoimmune diseases have evolved significantly, offering healthcare providers a range of tools to aid in accurate disease identification and monitoring. Traditional diagnostic approaches include blood tests to detect specific antibodies and inflammation markers associated with autoimmune diseases. However, recent advancements have introduced molecular and genetic testing, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and next-generation sequencing (NGS), which provide deeper insights into disease mechanisms and personalized treatment options.
The introduction of biomarker-based assays has also improved diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. Biomarkers specific to certain autoimmune diseases allow for quicker identification and differentiation from other conditions with similar symptoms. For example, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies are highly specific for RA, aiding in early and precise diagnosis even before joint damage becomes evident.
Market Segmentation
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): As one of the most prevalent autoimmune diseases, RA accounts for a significant portion of the autoimmune disease diagnosis market. Diagnostic tests for RA include rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-CCP antibodies, among others.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): Diagnosis of SLE involves a combination of clinical symptoms and laboratory tests, including antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and specific autoantibodies like anti-dsDNA.
Thyroiditis: This includes autoimmune thyroid diseases such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease, diagnosed through thyroid function tests (TFTs) and antibodies against thyroid peroxidase (TPO) and thyroglobulin (TG).
Scleroderma: Diagnostic approaches for scleroderma focus on clinical evaluation and antibody testing, including anti-Scl-70 and anti-centromere antibodies.
Market Size and Growth Prospects
The global autoimmune disease diagnosis market is projected to grow substantially over the coming years, driven by technological advancements, increasing disease prevalence, and the rising adoption of personalized medicine approaches. According to recent market research reports, the market size for autoimmune disease diagnostics is estimated to reach USD XX billion by 2028, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of XX% from 2021 to 2028.
North America currently dominates the market due to higher healthcare spending and a well-established healthcare infrastructure. However, Asia-Pacific and Latin American regions are expected to witness significant growth due to improving healthcare access and rising awareness of autoimmune diseases.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite technological advancements, challenges persist in autoimmune disease diagnosis, including the complexity of disease presentation, overlapping symptoms with other conditions, and the need for improved specificity and sensitivity of diagnostic tests. Addressing these challenges presents opportunities for innovation in diagnostic technologies, such as point-of-care testing and novel biomarkers.
Moreover, the shift towards patient-centric healthcare and personalized medicine is driving the development of companion diagnostics and targeted therapies, further expanding the autoimmune disease diagnosis market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the autoimmune disease diagnosis market is poised for significant growth, driven by increasing disease prevalence, technological advancements in diagnostic tools, and the demand for personalized treatment approaches. With ongoing research and development efforts, the future holds promise for improved diagnostic accuracy and better outcomes for patients with autoimmune diseases. As healthcare systems worldwide focus on early detection and effective management, the landscape of autoimmune disease diagnosis continues to evolve, offering new opportunities for innovation and improved patient care.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spellen
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


