Regulatory Challenges in Transdermal Patch Development and Approval
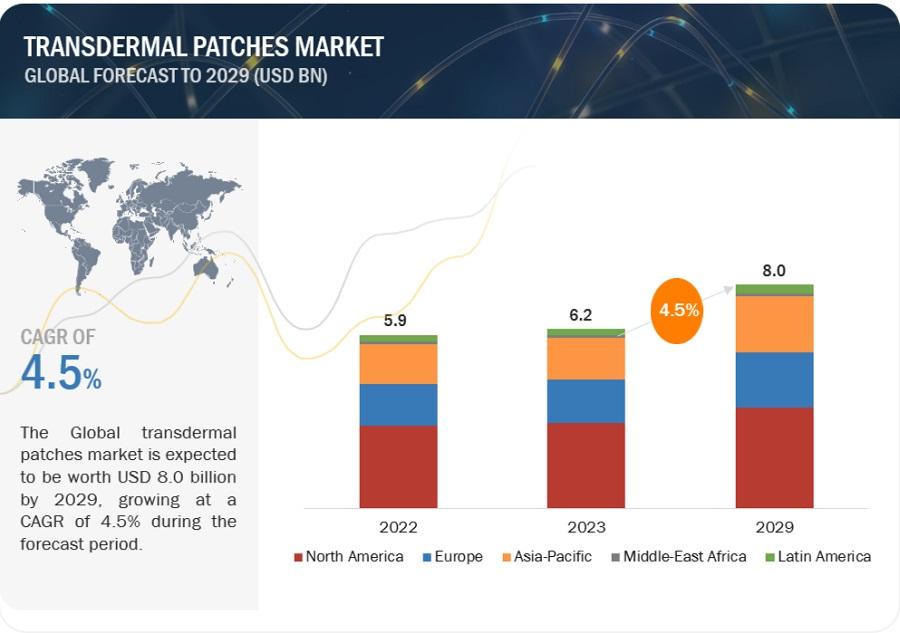
The transdermal patches market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by advancements in technology, an increasing number of chronic diseases, and a preference for non-invasive methods of drug delivery. Transdermal patches offer numerous benefits, including sustained release of medication, improved patient compliance, and reduced side effects compared to oral or injectable routes. This article explores the transdermal patches market by type, focusing on drug-in-adhesives, matrix, and reservoir membrane patches, and examines the factors influencing their adoption and market trends.
Transdermal Patches Market by Type (Drug-in-adhesives, Matrix, Reservoir Membrane) - Global Forecast to 2029
Transdermal patches market in terms of revenue was estimated to be worth $6.2 billion in 2023 and is poised to reach $8.0 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 4.5%
Download a PDF Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=190809043
Understanding Transdermal Patches
Transdermal patches are adhesive patches that deliver medication through the skin and into the bloodstream. They are designed to provide a controlled release of the drug over an extended period, ensuring a consistent therapeutic effect. These patches are used for a variety of medical conditions, including pain management, hormone replacement therapy, cardiovascular diseases, and nicotine addiction.
Types of Transdermal Patches
The transdermal patches market can be categorized into three primary types: drug-in-adhesives, matrix, and reservoir membrane patches. Each type has unique characteristics and applications, contributing to the market's diversity.
1. Drug-in-Adhesives
Drug-in-adhesive transdermal patches are the simplest form of transdermal systems. In these patches, the drug is directly incorporated into the adhesive that sticks the patch to the skin. This type is popular due to its straightforward manufacturing process and the ability to provide consistent drug release.
Advantages:
· Simplified manufacturing process
· Consistent and predictable drug release
· Thin and flexible design, enhancing patient comfort
Applications:
· Hormone replacement therapy (e.g., estradiol patches)
· Pain management (e.g., fentanyl patches)
· Nicotine addiction (e.g., nicotine patches)
Market Trends:
The drug-in-adhesives segment is expected to witness substantial growth due to its ease of use and the increasing prevalence of chronic conditions requiring long-term medication.
2. Matrix Patches
Matrix transdermal patches consist of a drug-loaded matrix layer sandwiched between the backing and the release liner. The drug is dispersed in a polymer matrix, allowing for controlled release over time. The matrix system is versatile and can accommodate a wide range of drugs.
Advantages:
· Controlled and sustained drug release
· Can deliver a variety of drug molecules
· Reduced risk of dose dumping
Applications:
· Chronic pain management (e.g., buprenorphine patches)
· Cardiovascular diseases (e.g., nitroglycerin patches)
· Neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., rivastigmine patches)
Market Trends:
The matrix patches segment is poised for growth due to their versatility and the increasing demand for long-acting medications. Innovations in polymer technology are also enhancing the efficacy and safety of these patches.
3. Reservoir Membrane Patches
Reservoir membrane patches consist of a liquid or gel drug reservoir enclosed by a rate-controlling membrane. This design allows for precise control over the drug release rate. Reservoir patches are often used for potent drugs that require careful dosing.
Advantages:
· Precise control over drug release
· Suitable for potent drugs with narrow therapeutic windows
· Can be designed for multi-day use
Applications:
· Hormone replacement therapy (e.g., testosterone patches)
· Chronic pain management (e.g., fentanyl patches)
· Cardiovascular diseases (e.g., clonidine patches)
Market Trends:
The reservoir membrane patches segment is expected to grow steadily due to the need for precise dosing in potent medications and the increasing prevalence of conditions requiring long-term treatment.
Market Dynamics and Drivers
Several factors are driving the growth of the transdermal patches market. These include the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, technological advancements, and the benefits associated with transdermal drug delivery systems.
Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases:
Chronic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer are on the rise globally. Transdermal patches offer a convenient and effective method for managing these conditions, driving their adoption in the market.
Technological Advancements:
Advancements in transdermal delivery technologies, such as microneedles and iontophoresis, are enhancing the efficacy and safety of transdermal patches. These innovations are expanding the range of drugs that can be delivered transdermally and improving patient outcomes.
Benefits of Transdermal Drug Delivery:
Transdermal patches provide several advantages over traditional drug delivery methods. They offer sustained release of medication, improved patient compliance, and reduced gastrointestinal side effects. These benefits are particularly important for patients requiring long-term therapy.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the transdermal patches market is growing, it also faces certain challenges. These include skin irritation, limited permeability of certain drugs, and regulatory hurdles. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation.
Skin Irritation:
Some patients may experience skin irritation or allergic reactions to the adhesive or drug formulation. Developing hypoallergenic adhesives and improving patch materials can address this issue.
Drug Permeability:
Not all drugs are suitable for transdermal delivery due to their molecular size or lipophilicity. Advances in formulation techniques and the use of permeation enhancers can overcome these limitations.
Regulatory Hurdles:
The stringent regulatory requirements for transdermal patches can be a barrier to market entry. However, demonstrating the safety and efficacy of these systems through robust clinical trials can facilitate regulatory approval and market acceptance.
Conclusion
The transdermal patches market is poised for significant growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, technological advancements, and the benefits of transdermal drug delivery systems. The market is diverse, with drug-in-adhesives, matrix, and reservoir membrane patches each offering unique advantages and applications. Despite challenges such as skin irritation and regulatory hurdles, ongoing innovation and research are expected to overcome these obstacles, paving the way for new opportunities and continued market expansion. As the demand for non-invasive and effective drug delivery methods rises, the transdermal patches market is set to play a crucial role in modern healthcare.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jocuri
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Alte
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


