Overview
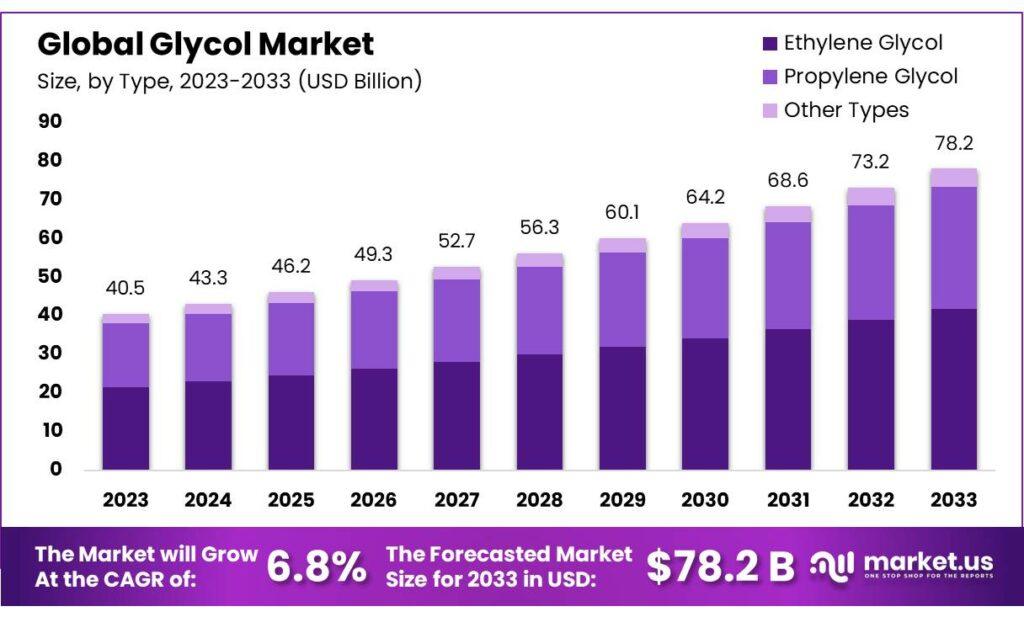
Glycol Market size is expected to be worth around USD 78.2 billion by 2033, from USD 40.5 Bn in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
The glycol market refers to the industry involved in the production, distribution, and sale of glycols, which are versatile chemicals widely used across various sectors. Glycols are organic compounds characterized by their hydroxyl (-OH) groups and are typically classified into two main types: ethylene glycol (EG) and propylene glycol (PG).
Ethylene glycol is primarily utilized as a raw material in the production of polyester fibers and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) resins, which are essential in the textile and packaging industries, respectively. It is also a key component in automotive antifreeze formulations due to its ability to lower the freezing point of water.
Propylene glycol, on the other hand, finds extensive application as a solvent, humectant, and coolant in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, cosmetics, and personal care products. Its hygroscopic properties make it valuable in products requiring moisture retention.
The glycol market is driven by diverse industrial applications, including its role in manufacturing processes, industrial fluids, and consumer products. Factors influencing market dynamics include raw material availability, technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and consumer preferences for sustainable and bio-based glycols.
Кеу Маrkеt Ѕеgmеntѕ
By Type
-
Ethylene Glycol
-
Monoethylene Glycol (MEG)
-
Diethylene Glycol (DEG)
-
Triethylene Glycol (TEG)
-
End-user Industry
-
Automotive
-
Auto Retail
-
Auto Traditional
-
Heavy-duty
-
Specialty Applications
-
-
HVAC
-
Textiles
-
Airlines
-
Medical
-
Pipeline Maintenance
-
Polyester Fibers & Resins
-
Food & Beverage
-
Other Applications
Download a sample report in MINUTES@ https://market.us/report/glycol-market/request-sample/
In 2023, Ethylene Glycol dominated the glycol market with a 53.4% share, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. The Automotive and Transportation sector led the glycol market, accounting for 35.6% of the demand, primarily for its use as an antifreeze agent in automotive coolants.
Маrkеt Кеу Рlауеrѕ
-
Shell PLC
-
MEGlobal International FZE
-
Indorama Ventures Public Company Limited
-
Reliance Industries Limited
-
PETRONAS Chemicals Group
-
BASF
-
Sinopec
-
Royal Dutch Shell
-
Lotte Chemical
-
Ashland
-
Cargill
-
Univar
-
AkzoNobel
-
SABIC
-
Huntsman
-
Others
Drivers: The glycol market is driven by the growing reliance of the textile industry on glycols, especially ethylene glycol, for producing essential materials like polyester fibers, cellophane, and leather. Post-pandemic, countries like China, the EU, and India saw significant growth in textile production and exports, with India benefiting from government initiatives like mega textile parks and the Buy America Act waiver procedure, further boosting market growth.
Restraints: Health concerns related to excessive glycol consumption, which can pose significant health risks, are a major restraint. Regulatory guidelines, such as the WHO's limit of 25 mg/kg of body weight for daily glycol intake as a food additive, aim to ensure safety. These concerns necessitate consumer education and adherence to safety guidelines to mitigate the impact on market growth.
Opportunities: The automotive industry's increasing reliance on ethylene glycol presents a significant growth opportunity. Ethylene glycol's properties, such as its low freezing point, make it crucial for automotive applications, including as an antifreeze and coolant. As automotive technology advances, the demand for ethylene glycol is expected to surge, driving market expansion.
Challenges: The glycol market faces challenges from health concerns, fluctuating raw material prices, and environmental regulations. Addressing these issues requires innovation, regulatory compliance, and investment in sustainable technologies. Additionally, the market's dependence on specific industries like automotive and textiles makes it vulnerable to sector-specific fluctuations, necessitating adaptive strategies for sustained growth.