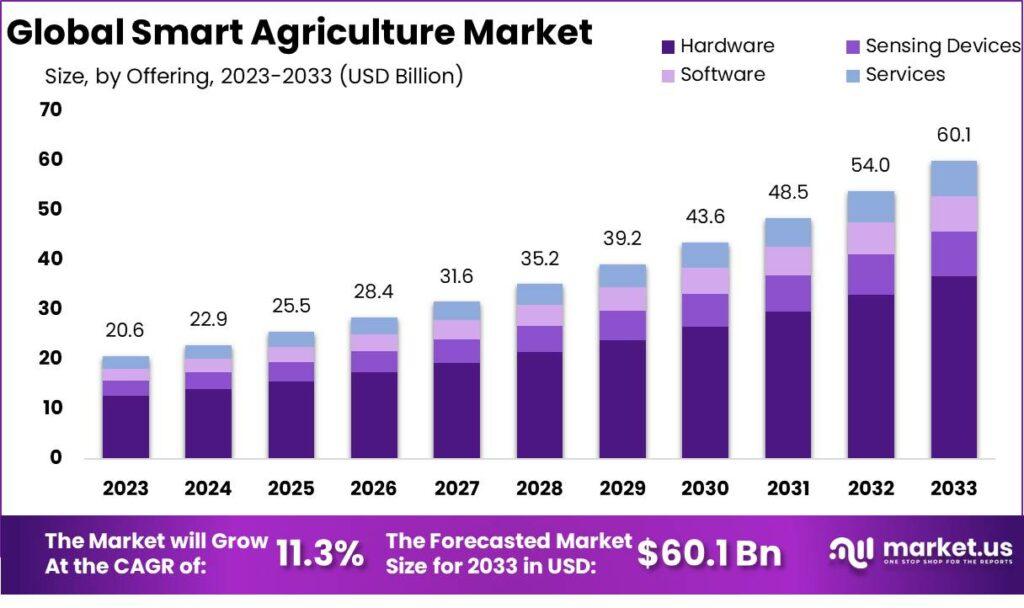
Smart Agriculture Market is anticipated to be USD 60.1 billion by 2033. It is estimated to record a steady CAGR of 11.3% in the Forecast period 2023 to 2033. It is likely to total USD 20.6 billion in 2023.
The smart agriculture market refers to the industry where advanced technologies like sensors, drones, and data analytics are used in farming to improve efficiency and sustainability. It's all about using these tools to gather real-time data from fields, helping farmers make informed decisions on irrigation, fertilization, pest control, and overall crop health. By integrating technology into agriculture, smart farming aims to maximize resources while reducing environmental impact and costs, and boosting productivity.
Download a sample report in MINUTES@ https://market.us/report/smart-agriculture-market/
This market has grown rapidly due to increasing global food demands and the push for sustainable farming practices. Technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) are crucial here, connecting devices that monitor soil conditions, crop health, and more. Precision farming, enabled by GPS and satellite imaging, allows farmers to manage their fields more precisely, using fertilizers and pesticides only where needed.
Automation with agriculture robots helps with tasks such as planting and harvesting, cutting labor costs and improving efficiency. Advanced data analytics and AI further enhance smart agriculture by processing large amounts of data to predict crop diseases, optimize irrigation, and suggest personalized farming strategies. Overall, the smart agriculture market is transforming how farming is done, making it more efficient, sustainable, and responsive to modern challenges.
Kеу Маrkеt Ѕеgmеntѕ
Hardware
-
HVAC system
-
LED grow lights
-
Valves & pumps
-
Sensors & control systems
-
Others
Sensing Devices
-
Soil sensor
-
Water sensors
-
Climate sensors
-
Others
Software
-
Web-based
-
Cloud-based
Services
-
Data services
-
Analytics services
-
Farm operation services
-
Supply chain management services
-
Climate information services
-
Maintenance & support
-
Others
By Farm Size
-
Small
-
Medium
-
Large
By Application
-
Precision farming application
-
Yield monitoring
-
On-farm
-
Off-farm
-
Field mapping
-
Crop scouting
-
Weather tracking & forecasting
-
Others
-
-
Livestock monitoring application
-
Milk harvesting
-
Breeding management
-
Feeding management
-
Others
-
-
Smart greenhouse application
-
Water & fertilizer management
-
HVAC management
-
Others
-
-
Precision Aquaculture
-
Precision Forestry
-
Others
Hardware Analysis: In 2023, sensors & control systems dominated the Smart Agriculture market, enabling precise data-driven farming practices.
Sensing Devices Analysis: Soil sensors led the market, crucial for optimizing irrigation and maximizing crop yield through real-time soil data.
Software Analysis: Cloud-based solutions took the lead, offering scalable data management and analytics for efficient farming operations.
Services Analysis: Data services emerged prominently, facilitating informed decision-making with real-time insights on soil, weather, and crop health.
By Farm Size Analysis: Large farms dominated, leveraging scalable smart agriculture solutions to enhance production efficiency.
By Application Analysis: Precision farming led, utilizing technologies like GPS and drones to optimize crop management and resource use.
Top Key Рlауеrѕ:
-
Autonomous Solutions, Inc.
-
GEA Group Aktiengesellschaft
-
CropMetrics LLC
-
Ag Leader Technology
-
BouMatic Robotic B.V.
-
Raven Industries
-
Argus Control Systems Ltd
-
Grownetics, Inc.
-
DeLaval Inc
-
DICKEY-john
-
AgJunction, Inc.
-
Farmers Edge Inc
-
Gamaya
-
Deere & Company
-
CropZilla
-
Topcon Positioning Systems
-
DroneDeploy
-
Granular, Inc.
-
Trimble Inc.
-
CLAAS KGaA mbH
Drivers:
Precision Farming Advancements: Smart agriculture technologies enable precise crop management through real-time data on climate, soil health, and crop conditions, boosting yields and resource efficiency. Rising Global Food Demand: Increasing population necessitates higher agricultural productivity and sustainable farming methods, which smart agriculture can support.
Restraints:
High Initial Costs: Adoption requires significant investments in technology, which can be prohibitive for small-scale farmers. Data Privacy Concerns: Collection and sharing of sensitive agricultural data raise privacy and cybersecurity issues. Limited Connectivity: Rural areas often lack adequate internet access, hindering technology adoption.
Opportunities:
IoT Integration: Growth potential lies in integrating IoT for real-time crop and equipment data. Blockchain for Transparency: Blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency, building consumer trust. Collaboration with AgriTech Startups: Partnerships can drive innovation and market expansion.
Challenges:
High Initial Costs: Affordability remains a barrier, particularly in developing regions. Data Security: Protecting sensitive agricultural data is critical for maintaining farmer trust. Connectivity Issues: Limited internet access in rural areas hampers technology effectiveness. Skills Development: Educating farmers on new technologies is essential but requires resources and time.