Quantum Dot Solar Cell Market Size, Share, Growth and Forecast to 2032
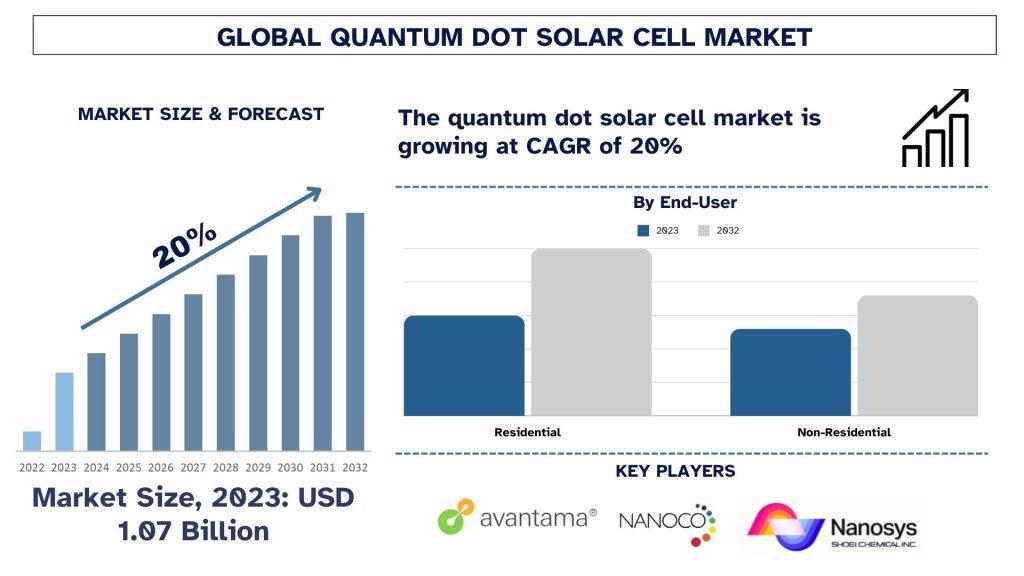
According to a new report by UnivDatos Market Insights, the Quantum Dot Solar Cell Market is expected to reach USD - Billion by 2032 by growing at a CAGR of ~20.0%.
Introduction
Quantum dot solar cell (QDSC) represents an emerging category in the solar energy industry across the globe. Quantum dot solar cells use Quantum dots, very small semiconductor crystals of about a few nanometres in size which help in capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity. Such cells have numerous advantages in comparison with the classical Si photovoltaic cells, for example, the possibilities of widening the range of light wavelengths to be converted into electric power, the potential for the creation of more effective solar converters, and the opportunities for the variety of shapes and uses of these cells. Some advantages of the quantum dot include its characteristic of tunable bandgap which enables it to absorb more sunlight and produce electricity at different times in the day or even at dawn, dusk, or at night.
Quantum dot solar cells are still under research and development, but their potential has made them one of the most promising breakthroughs in the solar power industry. The present article reveals the emerging trends, versatility, variety, material employed in the quantum dot solar cell, and market potential in the global scenario.
Request Free Sample Pages with Graphs and Figures Here - https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=12899
Demand Dynamics
There are several reasons why the demand for quantum dot solar cells is increasing: increasing demand for renewable energy sources, inherent shortcomings of silicon-based solar cells, and the development of nanotechnology and quantum mechanics. Researchers believe that because of quantum dots, the efficiency of the solar cell can be boosted thus enhancing the use of solar energy that is cheaper than other sources of energy.
The first external influence is contributing to the increasing demand as most countries and industries look to switch from fossil fuels to green energy. Wind and solar are enjoying popularity due to Governments’ encouragement of clean energy use and solar has become one of the most successful solutions – quantum dot cells feature better performance characteristics.
In addition, quantum dot solar cells have the capability of being incorporated into a huge spectrum of industries for residential and commercial use as well as portable electronic devices. This flexibility is driving demand as organizations seek to make use of solar in a manner other than by installation of rooftop panels.
Quantum Dot Solar Cells and Its Distinct Applications
Quantum dot solar cells have many uses, as the development progresses more uses are anticipated. Some of the most notable applications include:
Residential Solar Energy Systems: With quantum dot solar cells it is possible to develop solar panels for rooftops to provide electricity to homes. One of the advantages of these panels is that they can collect light even in conditions that are not very bright, therefore they are suitable for use at homes, especially in areas where the sun is not very vibrant.
Commercial and Industrial Energy Systems: Large-scale energy production is essential in commercial and industrial buildings; thus, quantum dot solar cells are advantageous. Such cells can help to save energy and minimize the usage of standard electrical networks as the source of power supply.
Wearable and Portable Electronics: When incorporated into solar cells, quantum dots in solar cells are small and lightweight, and hence, easily applicable in wearable technologies like smartwatches, fitness tracking devices, and wearable solar-powered apparel. They are also employed where renewable energy is needed on the go such as portable chargers and other small gadgets.
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): Quite probably, one of the most thrilling applications of quantum dot solar cells is the incorporation of the latter into the constructions of various structures. Since quantum dot solar cells can be integrated into windows, facades, and any other surface of the building, it makes it possible for such structures to produce electrical energy while at the same time having an excellent look.
Automotive Industry: In electric vehicles (EVs), the quantum dot solar cells aim at generating additional power for the battery and this would lead to the enhancement of the vehicles’ performance, and therefore the frequency of recharging would be less.
Space Applications: Due to their lightweight and high-efficiency qualities quantum dot solar cells can be very effectively used for powering spacecraft and satellites.
Quantity dot solar cells have been categorized as different types with different characteristics due to the materials used or the technology used in the construction of the cell. Some of the key types include:
Colloidal Quantum Dot Solar Cells (CQDSCs): These cells use colloidal quantum dots which dissolve in solution and are then set down onto a surface to create a layer. Compared to normal solar cells, CQDSCs are very easy to produce, and their production cost is relatively low.
Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cells (QDSSCs): Quantum dot-sensitized solar cells are quite close to dye-sensitized solar cells, however, the sensitizers used in the former are quantum dots. These cells can thus capture light in a broader range hence improving the energy conversion efficiency.
Perovskite-Quantum Dot Hybrid Solar Cells: Researchers call this type of solar cell ‘Perovskite / Quantum dot solar cells’, simply because it uses a combination of Quantum dots and perovskite solar technology which is famed for its ability to capture light. These two materials when combined lead to higher energy conversion and efficiency of the solar panel.
Core-Shell Quantum Dot Solar Cells: These cells are made of a core, composed of particles known as quantum dots and a shell that is of another type of semiconductor. This shell shelters the core made of quantum dot and maintains the stability of the core thereby increasing the efficiency and the sturdiness of the solar cell.
This is because the efficiency of osolar dot solar cells depends on the kind of materials that are used in the process of manufacturing the solar cells.
Materials that are used in the quantum dot cells for solar power are very important in the results and efficiency of the cells. Mainly, quantum dots are made from semiconductor materials, however, quantum dots can be of any other material based on specific applications and desired performance. Some of the key materials used in QDSCs include:
Cadmium Selenide (CdSe) Quantum Dots: Cadmium selenide is one of the most frequently utilized materials in the case of quantum dots owing to its capacity to trap a great range of sunlight wavelengths. However, cadmium has been reported to be toxic and hence there has been a search for new materials.
Lead Sulfide (PbS) Quantum Dots: Quantum dots of lead sulfide are employed in solar cells because they can absorb the infrared light which is normally captured by the conventional solar cell. This property helps the PbS-based quantum dot solar cells to attain better efficiencies.
Copper Indium Selenide (CIS) Quantum Dots: Copper indium selenide QDs are less toxic as compared to cadmium-based quantum dots. They have comparable levels of efficiency except that the former is less hazardous to the environment.
Perovskites: Quantum dots increase the light-absorbing properties of the solar cell and when incorporated with perovskite materials they further improve. Perovskite-quantum dot hybrid solar cells are quite common these days, especially since they provide high efficiency and the chances of low-cost modules.
Related Reports-
Carbon Offset and Carbon Credit Trading Service Market: Current Analysis and Forecast (2024-2032)
Biopellet Energy Market: Current Analysis and Forecast (2024-2032)
Conclusion
The global quantum dot solar cell market is poised for substantial growth as advancements in nanotechnology and quantum mechanics continue to unlock new possibilities for solar energy generation. The demand for more efficient, flexible, and cost-effective solar technologies is driving investment in QDSC research and development, with applications ranging from residential solar panels to wearable electronics and space exploration.
Quantum dot solar cells offer several key advantages over traditional solar technologies, including the ability to capture a broader spectrum of light, improved performance in low-light conditions, and the potential for lower production costs. However, challenges remain, such as the need to address the environmental concerns associated with certain materials and the scalability of production processes.
As governments, industries, and consumers increasingly embrace renewable energy, quantum dot solar cells are expected to play a significant role in shaping the future of the solar power industry. Continued innovation in materials and manufacturing techniques will be critical to realizing the full potential of this promising technology, positioning quantum dot solar cells as a key contributor to the global energy transition.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Giochi
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Altre informazioni
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


