Metal-Organic Framework: Transforming Material Science and Technology
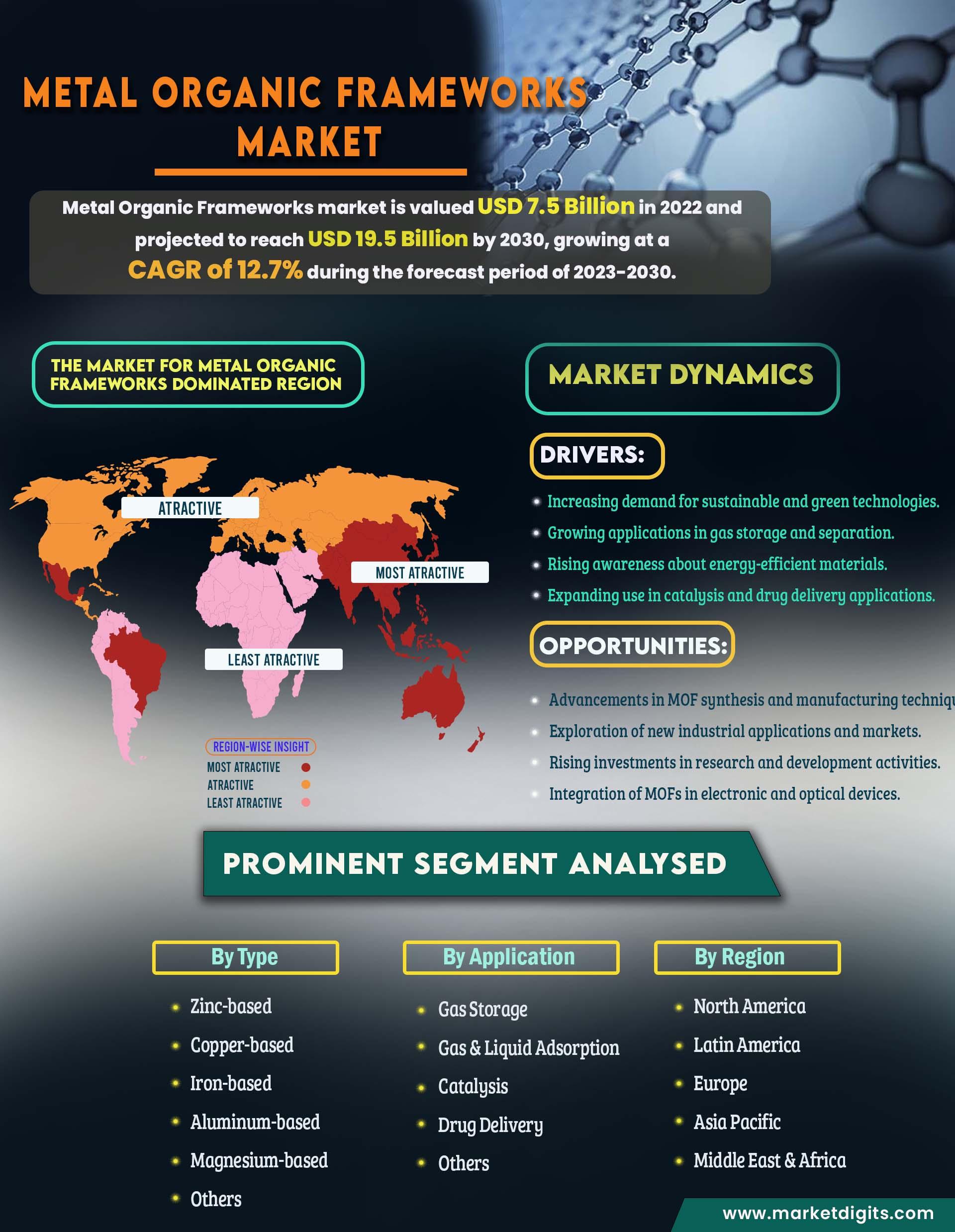 Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) are an innovative class of porous materials constructed from metal ions or clusters coordinated to organic ligands. These materials have garnered significant attention due to their versatile structure and remarkable properties. MOFs' unique ability to form highly porous frameworks with enormous surface areas makes them ideal for a range of applications, including gas storage, separation, and catalysis. For example, MOFs can efficiently store gases like hydrogen or methane, offering potential solutions for clean energy storage. Additionally, their tunable pore sizes and functional groups enable selective gas separation, making them valuable for industrial processes and environmental remediation. Beyond gas-related applications, MOFs are also being explored in drug delivery systems, where their ability to encapsulate and release therapeutic molecules in a controlled manner can enhance drug efficacy and reduce side effects. In the field of catalysis, MOFs' high surface area and the presence of active sites facilitate efficient catalytic reactions, driving advancements in chemical synthesis and renewable energy production. As research progresses, the potential applications of MOFs continue to expand, positioning them as a transformative material in various scientific and industrial fields. With ongoing innovation, MOFs are set to play a pivotal role in addressing some of the most pressing challenges of our time.
Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) are an innovative class of porous materials constructed from metal ions or clusters coordinated to organic ligands. These materials have garnered significant attention due to their versatile structure and remarkable properties. MOFs' unique ability to form highly porous frameworks with enormous surface areas makes them ideal for a range of applications, including gas storage, separation, and catalysis. For example, MOFs can efficiently store gases like hydrogen or methane, offering potential solutions for clean energy storage. Additionally, their tunable pore sizes and functional groups enable selective gas separation, making them valuable for industrial processes and environmental remediation. Beyond gas-related applications, MOFs are also being explored in drug delivery systems, where their ability to encapsulate and release therapeutic molecules in a controlled manner can enhance drug efficacy and reduce side effects. In the field of catalysis, MOFs' high surface area and the presence of active sites facilitate efficient catalytic reactions, driving advancements in chemical synthesis and renewable energy production. As research progresses, the potential applications of MOFs continue to expand, positioning them as a transformative material in various scientific and industrial fields. With ongoing innovation, MOFs are set to play a pivotal role in addressing some of the most pressing challenges of our time.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


