Heparin is an essential anticoagulant used to prevent and treat blood clots in various medical conditions, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and during surgeries. It works by inhibiting certain proteins involved in blood clotting, reducing the risk of clot formation. As a widely used blood thinner, heparin plays a critical role in both inpatient and outpatient settings, especially in high-risk procedures like heart surgeries, dialysis, and post-operative care. Heparin is administered intravenously or subcutaneously and requires careful monitoring to avoid complications like bleeding. Despite the rise of alternative anticoagulants, heparin remains a cornerstone in anticoagulation therapy due to its proven efficacy and cost-effectiveness.
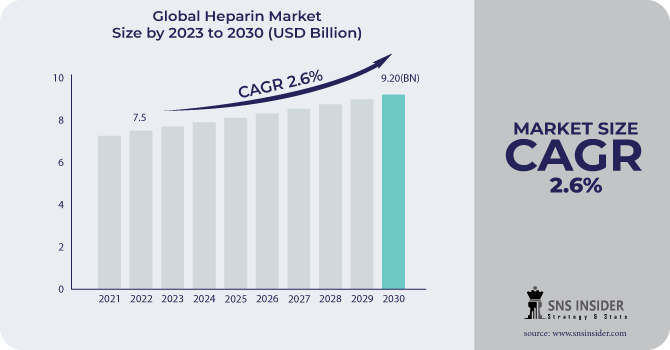
The Heparin Market was estimated at USD 7.71 billion in 2023 and is poised to reach 9.61 billion in 2031 anticipated to expand at a compound annual growth rate approx. CAGR of 2.8% for the forecast period of 2024-2031.
Future Scope:
The future of heparin therapy is focused on improving safety and minimizing side effects, particularly the risk of bleeding. Researchers are exploring ways to improve heparin’s specificity to target clotting factors more precisely, reducing the chances of adverse effects. The development of low molecular weight heparins (LMWHs) has already led to better management of blood clotting, offering advantages like more predictable dosing and fewer monitoring requirements. Another promising area is the exploration of heparin alternatives that could be used in combination with or as substitutes for traditional heparin. Additionally, advancements in biotechnology and nanomedicine may lead to the creation of more advanced formulations of heparin that improve its bioavailability and reduce complications.
Emerging Trends:
A key emerging trend in heparin therapy is the use of low molecular weight heparins (LMWHs), which have been shown to be as effective as standard heparin but with fewer side effects, such as bleeding complications. Another trend is the increasing use of heparin-coated devices, like catheters and dialysis machines, to reduce clot formation in medical procedures. There is also growing interest in the development of heparin resistance testing, which aims to identify patients who may not respond to standard heparin doses, enabling more personalized anticoagulation therapy. Furthermore, research into oral anticoagulants as a replacement for injectable heparin is accelerating, although heparin’s position in acute care remains vital for now.
Applications:
Heparin is used in a variety of clinical applications. It is commonly administered during surgical procedures, particularly cardiac surgeries, to prevent clot formation. Dialysis patients also rely on heparin to prevent clotting during kidney dialysis. Heparin is vital in treating and preventing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), which can result from immobility after surgery or prolonged hospital stays. Additionally, heparin therapy is often used in managing acute coronary syndrome (ACS), such as heart attacks and unstable angina, where rapid anticoagulation is required to prevent further clotting.
Key Points:
· Heparin is a critical anticoagulant used to prevent and treat blood clots.
· Low molecular weight heparins (LMWHs) offer advantages in safety and ease of use.
· Heparin-coated medical devices reduce clotting during medical procedures.
· Personalized anticoagulation therapy is gaining momentum with heparin resistance testing.
· Advances in biotechnology may lead to improved formulations of heparin for safer and more effective use.
Conclusion:
Heparin remains a cornerstone of anticoagulation therapy due to its effectiveness and critical role in managing blood clotting disorders. As medical research advances, new formulations and alternative therapies are emerging, offering the promise of more tailored treatments with fewer complications. Heparin’s role in preventing and managing blood clots will continue to evolve, ensuring that it remains an essential component in modern medicine for years to come.
Read More Details: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/heparin-market-2975
Contact Us:
Akash Anand — Head of Business Development & Strategy
Email: info@snsinsider.com
Phone: +1–415–230–0044 (US) | +91–7798602273 (IND)