Cyanic acid is a colorless toxic liquid with a boiling point of 23.5 ℃ and a melting point of - 81 ℃. Cyanide is converted to cyanamide at 0 ℃.
In water, cyanic acid is hydrolyzed to carbon dioxide and ammonia.
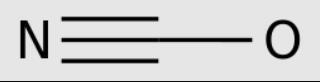
Cyanic acid (H-O-C ≡ N) is the isomer of fulvic acid (H-C=N-o).
There are tautomers of cyanic acid, H-N=C=O and isoCyanic acid.
It is formed by the reaction of potassium Cyanic acid and formic acid.
The trimer of cyanic acid is cyanuric acid.
Cyanic acid is the simplest and most stable compound. It contains carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen, the four most common atoms in organic chemistry (thunderstorm instability).
Cyanic acid is a colorless toxic liquid with a boiling point of 23.5 ℃ and a melting point of - 81 ℃. Cyanide is converted to cyanamide at 0 ℃.
In water, cyanic acid is hydrolyzed to carbon dioxide and ammonia.
Cyanic acid (H-O-C ≡ N) is the isomer of fulvic acid (H-C=N-o).
There are tautomers of cyanic acid, H-N=C=O and isoCyanic acid.
It is formed by the reaction of potassium Cyanic acid and formic acid.
The trimer of cyanic acid is cyanuric acid.
Cyanic acid is the simplest and most stable compound. It contains carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen, the four most common atoms in organic chemistry (thunderstorm instability).
Various reactions of cyanic acid with cyanic acid ions were studied. When hydrochloric acid or nitric acid is added, cyanic acid can be quantitatively decomposed into HNCO+H3O+→ CO2+NH4+. The rate constant of the reaction was measured within a certain range of temperature and ionic strength, and it was found that the rate constant of the reaction was 0.86 mol/L − 1 min. − 1 At unit ionic strength and 1.5 ℃. The effect of ionic strength on hydrochloric acid reaction is very similar to that on the activity coefficient of acid itself. When no acid is added, cyanic acid is decomposed into a first-order reaction: HNCO+2H2O → NH4HCO3, followed by a fast second-order reaction: NH4HCO3+HNCO → NH4NCO+H2CO3. The rate constant of this reaction is 0.011 minutes. − 1 at 0 ℃. The activation energy is 16 kcal. There are also several percent of side effects. The Cyanic acid ion in the alkaline solution is decomposed into OCN −+2H2O → NH4++CO3 − −. The reaction was investigated in a certain range of temperature and ionic strength: k=3.0 × 10 − 3 min is the first order reaction. − 1 at 100 ℃. (0.3 ionic strength) and 23.5 kcal activation energy. The rate depends on the concentration of hydroxide, when the concentration of hydroxide is very low. This reaction is catalyzed by carbonate rather than some other anions. The rate of catalytic reaction is proportional to the concentration of carbonate, but not related to Cyanic acid ester, at least in a large range. The ionization constant of cyanic acid was determined by avoiding hydrolysis error; The resulting value is 2.0 × 10−4。 The oxidation of hypochlorite and chlorine to Cyanic acid was briefly investigated.
From November 2018 to November 2011, China's total exports of Cyanic acid to the United States were 5711434KG, and the total exports were 31112641 US dollars. The largest share of exports in the past 12 months was 16.32% in 2018.11.
From 2018.11 to 2019.11, China's total exports of Cyanic acid were 126742366KG, and the total exports were 572301811 US dollars. The largest share of exports in the past 12 months was 11.53% in 2019.
From November 2018 to November 2019, China exported cyanic acid to 79 countries. The import volume from high to low is India, Britain, Japan, South Korea, Belgium, the United States, Germany, the Netherlands, Italy and Taiwan. China's exports to India are the highest, accounting for 18.59% of China's total exports.