The Impact of Rapid Prototyping Technology on Modern Manufacturing
In an era where speed and precision are key drivers in the success of new products, the advent of rapid prototyping technology has transformed how industries approach design, testing, and manufacturing. This innovative approach enables businesses to develop functional prototypes quickly, streamline product development processes, and bring ideas to life faster than ever before. From automotive to healthcare and electronics, rapid prototyping plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of manufacturing. This article explores the core principles of rapid prototyping technology, its major types, benefits, and its growing applications in various sectors.
What is Rapid Prototyping Technology?
Rapid prototyping (RP) refers to a collection of techniques used to quickly create a model or prototype of a product, part, or component from digital design data. This technology is employed to produce early physical models that allow designers and engineers to test their ideas, visualize product concepts, and assess functionality before proceeding to full-scale production.
Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, rapid prototyping eliminates the need for time-consuming and expensive tooling. By using computer-aided design (CAD) files, these technologies can quickly convert a digital design into a tangible prototype, enabling businesses to test, modify, and refine their ideas with minimal lead time and cost.
Key Technologies Behind Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping encompasses various techniques that cater to different design needs and production capabilities. Some of the most notable technologies include:
1. 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
3D printing is perhaps the most well-known and widely used form of rapid prototyping. This process builds objects layer by layer using materials like plastic, metal, or resin. The digital 3D model is translated into a machine-readable format, and the printer creates the part by fusing material one thin layer at a time.
One of the biggest advantages of 3D printing is its ability to produce highly complex geometries that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. It is also highly customizable, making it ideal for producing one-off prototypes or low-volume production runs.
Some common types of 3D printing technologies used in prototyping include:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): A popular technique that uses a thermoplastic filament heated and extruded through a nozzle to create layers.
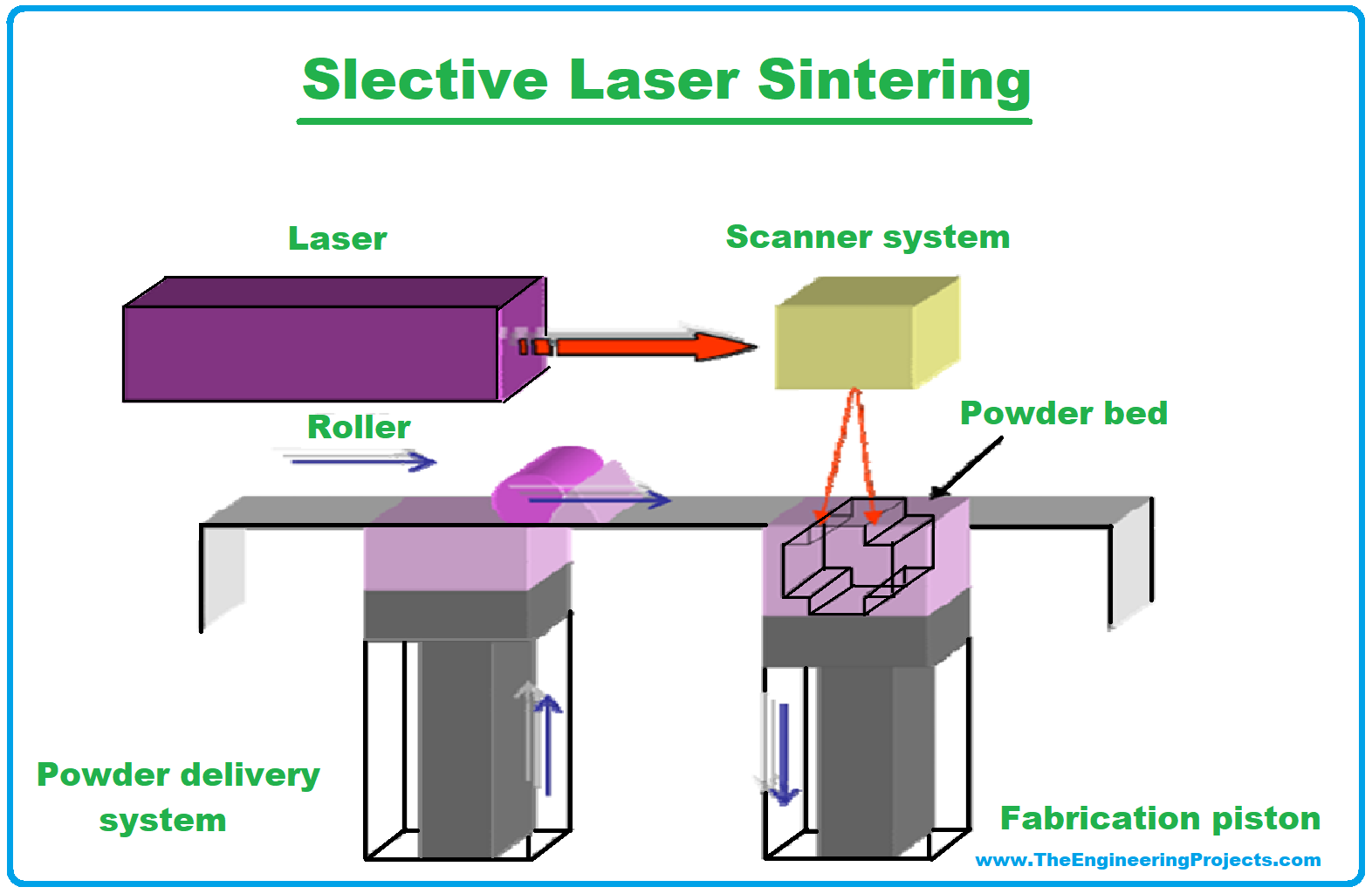
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): A laser is used to fuse powdered materials (like plastic, metal, or ceramic) to form solid parts.
- Stereolithography (SLA): A laser is used to cure liquid resin into solid layers to form highly detailed prototypes.
2. CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining involves a computer-controlled tool (e.g., a drill or lathe) that cuts and shapes material from a solid block to create parts with high precision. Unlike 3D printing, CNC machining is a subtractive process, meaning it removes material to form the desired shape.
CNC machining is especially useful when a part needs to be made from metals or other hard materials and is often used for producing functional prototypes. It offers high accuracy and can create parts with excellent surface finishes, which is particularly important in industries such as aerospace and automotive.
3. Injection Molding
Injection molding is a widely used technique in mass production, but it also finds application in rapid prototyping. In injection molding, molten material (typically plastic) is injected into a mold to create the desired part. While mold creation used to be a time-intensive and costly process, recent advances have made it possible to produce molds more quickly and cost-effectively, allowing rapid prototyping to benefit from this method as well.
Injection molding is ideal for creating parts with complex shapes and high-volume production. It is frequently used for products such as automotive components, consumer goods, and medical devices.
4. Laser Cutting and Etching
Laser cutting uses a focused beam of light to cut or engrave materials like plastic, wood, or metal. It is known for its precision and ability to handle intricate designs and patterns. Laser cutting is commonly used in prototyping for producing flat parts, enclosures, or intricate geometric designs that need a high degree of accuracy.
Laser cutting is often paired with other technologies, such as 3D printing, to produce parts that have both complex geometries and detailed engraving or etching.
5. Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting is a rapid prototyping method used to create functional prototypes in small quantities. It involves pouring liquid silicone or other materials into a mold that has been created using a 3D printed part or another prototype. Once the material hardens, it forms a precise copy of the original part.
Vacuum casting is often used when low-volume production is required, and it is particularly useful in industries like automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial design.
Benefits of Rapid Prototyping Technology
Rapid prototyping technology offers numerous advantages, making it indispensable in the design and manufacturing world. Some of the most significant benefits include:
1. Reduced Time-to-Market
One of the most compelling reasons to adopt rapid prototyping is its ability to drastically reduce product development timelines. By enabling faster iteration of prototypes, businesses can test and refine designs in a matter of days, rather than weeks or months. This speed allows companies to bring products to market much faster, gaining a competitive edge in industries where time is critical.
2. Cost Savings
Traditional prototyping methods often involve expensive tooling and setup costs, especially when creating molds or specialized manufacturing equipment. With rapid prototyping, there is no need for costly molds or tools, and designs can be produced using digital data alone. This leads to substantial cost savings, particularly for small businesses or startups with limited budgets.
Additionally, rapid prototyping allows for more efficient use of materials, as the process is often more accurate and less wasteful than traditional methods.
3. Improved Design Flexibility
The ability to quickly iterate on prototypes gives designers the flexibility to experiment with different designs and features. With rapid prototyping, businesses can quickly test new ideas, gather feedback, and refine products before committing to mass production. This flexibility allows for more creative and innovative designs that are better aligned with customer needs and market demands.
4. Enhanced Product Quality
By allowing for multiple rounds of testing and evaluation, rapid prototyping helps identify potential design flaws early in the development process. These prototypes can be tested for functionality, ergonomics, and performance, providing valuable insights that can be used to improve the final product. The ability to make design adjustments early helps reduce the risk of defects in the final production, leading to higher-quality products.
5. Customization and Personalization
For industries that require customized products, rapid prototyping technology offers a valuable solution. Whether in healthcare, consumer products, or automotive, rapid prototyping enables businesses to create personalized items that cater to specific needs. For example, in the medical field, rapid prototyping allows the creation of custom implants and prosthetics that are tailored to individual patients.
Applications of Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is utilized across various industries, each benefiting from the technology’s ability to accelerate development, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. Some notable applications include:
1. Automotive
The automotive industry has embraced rapid prototyping to speed up the design and testing of car parts, including engine components, safety features, and interior parts. Manufacturers can prototype and test parts before full-scale production, ensuring that each component meets quality standards and regulatory requirements.
2. Aerospace
In aerospace, rapid prototyping enables the creation of lightweight, durable parts and components used in aircraft and spacecraft. Engineers use rapid prototyping to create test models for parts like engine components, airframes, and even cabin interiors. Given the high-stakes nature of this industry, prototyping is essential for ensuring that parts perform reliably under extreme conditions.
3. Healthcare
Rapid prototyping has made a significant impact on healthcare, particularly in the development of customized medical devices and implants. For example, prosthetics and orthotics can be tailored to the unique anatomical needs of individual patients. Additionally, 3D-printed anatomical models are used for pre-surgical planning, helping surgeons practice complex procedures before performing them on patients.
4. Consumer Goods and Electronics
Consumer goods manufacturers use rapid prototyping to quickly test and refine product designs for everything from electronics to household items. Whether creating prototype enclosures, functional components, or entire products, rapid prototyping enables designers to bring their concepts to life quickly, reducing the time needed for market introduction.
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping technology has significantly changed the way industries approach product design and development. By enabling faster iterations, reducing costs, and improving product quality, it has become an essential tool in various sectors, from automotive and aerospace to healthcare and consumer goods. As the technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly unlock even more possibilities for innovation, efficiency, and customization, shaping the future of manufacturing and product development. With rapid prototyping, businesses can stay ahead of the curve, bringing better products to market faster and more affordably than ever before.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- الألعاب
- Gardening
- Health
- الرئيسية
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- أخرى
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


