Leprosy Drugs and Their Side Effects: What You Should Know
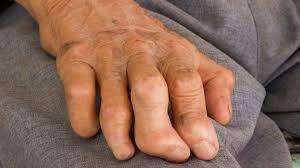
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease, is a chronic infectious condition caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae. This disease primarily affects the skin, peripheral nerves, mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, and the eyes.
Despite its historical stigma, leprosy is curable, especially when detected early. Understanding its occurrence, early signs, available leprosy treatments, and potential side effects of leprosy drugs is crucial for effective management.
How Leprosy Occurs
Leprosy is caused by the slow-growing bacterium Mycobacterium leprae. Transmission occurs through prolonged close contact with an untreated infected person, typically via respiratory droplets from the nose and mouth.
It's important to note that leprosy is not highly contagious; most people have a natural immunity to the disease.
Factors such as genetic predisposition and a weakened immune system can increase susceptibility. The bacterium primarily targets the skin and peripheral nerves, leading to the characteristic symptoms of the disease. The incubation period can vary widely, ranging from a few months to over 20 years, making it challenging to trace the exact source of infection.
Early Signs of Leprosy
Early detection of leprosy is vital for effective treatment and preventing complications. Initial symptoms often manifest as discolored skin patches that may be numb and less sensitive to temperature or touch. These patches can be lighter or darker than the surrounding skin and may appear on the face, arms, legs, or back.
As the disease progresses, individuals might experience muscle weakness, particularly in the hands and feet, leading to difficulty in performing everyday tasks. Thickening of the skin, especially on the face and earlobes, can occur, along with painless ulcers on the soles of the feet.
Nerve involvement may lead to a loss of sensation, increasing the risk of unnoticed injuries. Eye problems, such as dryness or reduced blinking, can also develop if the facial nerves are affected.
Recognizing these early signs and seeking prompt medical attention can prevent severe complications and transmission to others.
Medications for Leprosy and Their Side Effects
Leprosy is treated with a combination of antibiotics, a regimen known as multidrug therapy (MDT), which is highly effective in curing the disease and preventing transmission. The World Health Organization provides MDT free of charge to all patients worldwide. The specific leprosy drugs used depend on the form of the disease:
-
Paucibacillary Leprosy: This form is treated with two antibiotics: rifampicin and dapsone, administered over six months.
-
Multibacillary Leprosy: This more severe form requires three antibiotics: rifampicin, dapsone, and clofazimine, taken over 12 months.
While these leprosy treatments are effective, they can have side effects:
-
Rifampicin: May cause reddish-orange discoloration of bodily fluids, gastrointestinal disturbances, and, in rare cases, liver dysfunction.
-
Dapsone: Can lead to hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells), especially in individuals with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, and may cause allergic reactions.
-
Clofazimine: Often results in skin pigmentation, causing a reddish-brown discoloration, and can cause dryness and gastrointestinal issues.
It's essential for patients to be monitored regularly during treatment to manage these side effects effectively. Despite these potential adverse effects, the benefits of MDT in curing leprosy and preventing disability far outweigh the risks.
Conclusion
Leprosy is a curable disease, and early detection coupled with appropriate leprosy medication can prevent long-term complications. Awareness of the early signs and understanding the importance of completing the full course of medicine of leprosy are crucial steps in managing the disease effectively.
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure that any side effects from leprosy drugs are promptly addressed, leading to successful treatment outcomes.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jeux
- Gardening
- Health
- Domicile
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Autre
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology



.jpg)