Hyperhidrosis in Elderly People: Why It Happens and What to Do
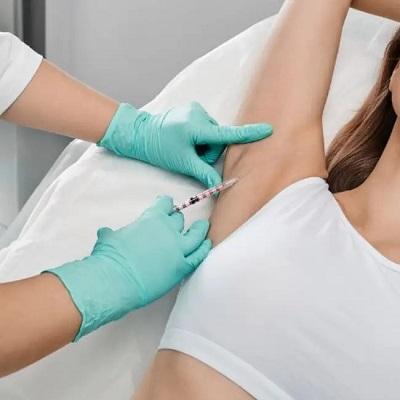
Sweating is a natural function that helps regulate body temperature, but excessive sweating, known as hyperhidrosis, can be a significant concern for elderly individuals. While hyperhidrosis is often associated with younger people, it can persist or even develop later in life due to various underlying factors. Finding the right Hyperhidrosis Treatment in Oman is crucial for seniors dealing with excessive sweating, as it can greatly impact their comfort, social life, and overall well-being.
Older adults experiencing hyperhidrosis may notice excessive sweating in specific areas like the hands, feet, and underarms or widespread sweating affecting the entire body. Unlike younger individuals, elderly people with hyperhidrosis often have additional health conditions that complicate treatment. With the right Hyperhidrosis Treatment Oman, seniors can find relief and improve their quality of life through medical therapies and lifestyle changes.
Understanding Hyperhidrosis in the Elderly:
Hyperhidrosis in older adults can be classified into two types:
Primary Hyperhidrosis:
- Typically starts in adolescence or early adulthood and may persist into old age.
- Affects specific areas like the hands, feet, underarms, or face.
- Caused by overactive sweat glands triggered by the nervous system.
Secondary Hyperhidrosis:
- Develops later in life due to underlying medical conditions.
- Can be triggered by medications, metabolic disorders, or neurological issues.
- Often results in generalized sweating affecting the whole body.
Common Causes of Hyperhidrosis in Elderly People:
Older adults may develop hyperhidrosis due to various medical conditions, lifestyle factors, and physiological changes. Identifying the cause helps determine the best course of treatment.
1. Age-Related Changes in the Nervous System:
- The autonomic nervous system, which controls sweating, may become dysregulated with age.
- Overactive nerve signals lead to excessive sweating even when the body does not need to cool down.
2. Medications That Cause Excessive Sweating:
- Blood pressure medications (beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers).
- Antidepressants and psychiatric medications.
- Pain relievers such as opioids.
- Medications for Parkinson’s disease or diabetes.
3. Underlying Medical Conditions:
- Diabetes – Uncontrolled blood sugar can affect nerve function and trigger excessive sweating.
- Menopause & Hormonal Imbalances – Sudden hot flashes and night sweats are common in older women.
- Parkinson’s Disease – Affects the nervous system and can lead to abnormal sweating patterns.
- Hyperthyroidism – An overactive thyroid increases metabolism and sweating.
4. Obesity and Poor Circulation:
- Excess body weight contributes to higher body temperature and increased sweating.
- Poor circulation in the elderly can lead to improper body temperature regulation.
Symptoms of Hyperhidrosis in Older Adults:
Hyperhidrosis presents differently in elderly people compared to younger individuals. Recognizing symptoms can help seniors seek timely treatment.
Typical Signs of Hyperhidrosis in Seniors:
- Excessive sweating that occurs even in cool environments.
- Profuse night sweating that disrupts sleep.
- Clammy hands and feet, making it difficult to hold objects.
- Persistent sweating despite resting or staying hydrated.
How Hyperhidrosis Affects the Daily Life of Seniors:
The impact of hyperhidrosis extends beyond physical discomfort, affecting mental health and daily routines.
1. Social and Emotional Challenges:
- Embarrassment in social settings due to visible sweat stains.
- Increased anxiety, especially in public situations.
- Isolation or reluctance to participate in activities.
2. Physical Health Risks:
- Dehydration due to excessive fluid loss.
- Increased risk of fungal infections, particularly in the feet.
- Skin irritation and rashes from prolonged dampness.
Hyperhidrosis Treatment Options for Elderly People in Oman:
Finding the right treatment is essential to managing hyperhidrosis in older adults effectively.
1. Clinical Antiperspirants:
- Prescription-strength aluminum chloride solutions can block sweat glands.
- Best suited for localized sweating in areas like hands, feet, and underarms.
2. Oral Medications:
- Anticholinergics (e.g., glycopyrrolate) reduce nerve signals responsible for sweating.
- Beta-blockers help manage stress-induced sweating.
- Medications should be used cautiously due to potential side effects like dry mouth or dizziness.
3. Iontophoresis Therapy:
- Uses mild electrical currents to temporarily disable sweat glands.
- Effective for hand and foot sweating.
4. Botox Injections:
- Blocks nerve signals that cause excessive sweating.
- Provides relief for 6-12 months, but requires repeat treatments.
5. miraDry (Microwave Thermolysis):
- Destroys sweat glands in the underarms permanently.
- Safe and effective for seniors who do not respond to other treatments.
6. Surgery (ETS – Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy):
- Considered a last resort for severe cases
- Permanently interrupts nerve signals that cause excessive sweating.
Daily Management Strategies for Seniors with Hyperhidrosis:
In addition to medical treatments, adopting practical lifestyle habits can help seniors manage excessive sweating.
1. Clothing & Personal Care Tips:
- Wear breathable, moisture-wicking fabrics to stay dry.
- Use absorbent underarm pads to prevent sweat stains.
- Keep the skin dry with talcum powders or cornstarch.
2. Hydration & Diet Adjustments:
- Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration.
- Avoid spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol, which can trigger sweating.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
3. Stress & Anxiety Management:
- Practice deep breathing exercises and meditation.
- Engage in relaxing activities like gentle yoga or nature walks.
- Seek emotional support through counseling or support groups.
Final Thoughts:
Hyperhidrosis in elderly people can be frustrating, uncomfortable, and socially isolating, but effective treatments are available. With the right Hyperhidrosis Treatment Oman, seniors can manage their symptoms and improve their daily comfort. Whether through medical therapies, lifestyle modifications, or stress-reducing techniques, taking proactive steps can help older adults live confidently without the burden of excessive sweating.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- IT, Cloud, Software and Technology


