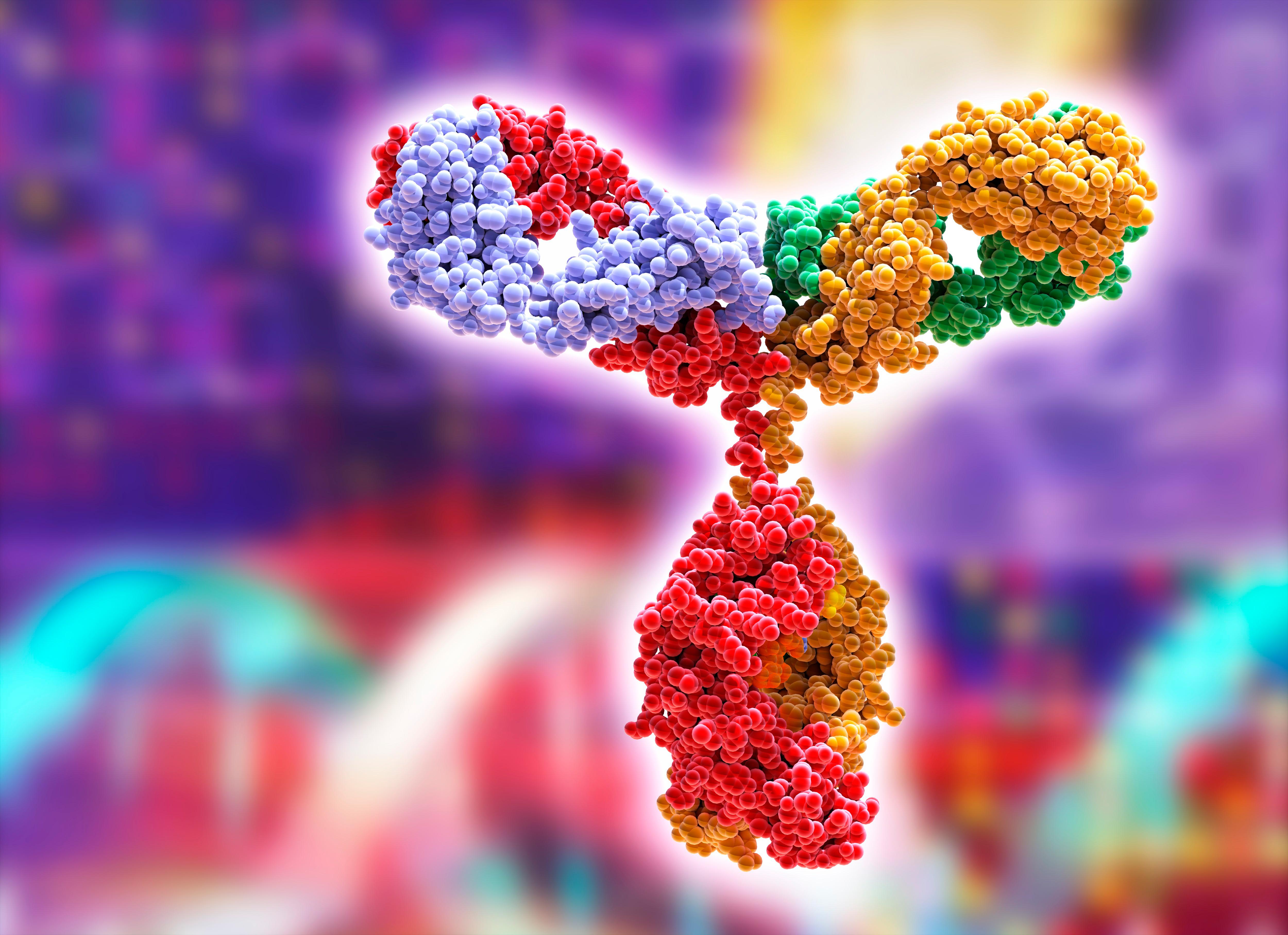
The science of immunoglobulin delves into the fascinating world of antibody function and its critical role in the immune system. Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are protein molecules produced by B cells that recognize and bind to specific foreign substances, known as antigens. Understanding the intricacies of antibody function is crucial for unraveling the secrets of how our immune system defends against pathogens and maintains overall health.
Immunoglobulin are highly specialized molecules that consist of two heavy chains and two light chains, forming a Y-shaped structure. Each antibody has a unique antigen-binding site at the tips of the Y arms, enabling it to recognize and neutralize specific antigens. Antibodies can act through various mechanisms, including neutralization of pathogens, activation of complement system, recruitment of immune cells, and enhancement of phagocytosis. Studying the science of immunoglobulin helps us gain insights into the diverse functions and roles antibodies play in immune responses. It allows us to understand how antibodies contribute to immunity, vaccination, allergic reactions, autoimmune diseases, and other immune-related processes. By unraveling the secrets of antibody function, scientists can further harness this knowledge to develop innovative therapies and treatments for various immune-related disorders.
Read More:
https://bloggers-vision.blogspot.com/2023/06/immunoglobulin-rising-trend-in.html